Views: 10

Philosophy, Politics, Education, Ethics, Psychology, Religion, Psychoanalysis, Aesthetics, Humanism, The Arts, Ancient Greek Philosophy, Enlightenment Philosophy. A site dedicated to the humanistic art of lecturing and the synthesis of Aristotelian, Kantian, and Wittgensteinian Philosophy: The Pre-Socratics, Socrates, Plato, The scholastics, Descartes, Spinoza, Hobbes, Hume, Heidegger, Freud, Arendt, Sartre, Merleau-Ponty, Ricoeur, Jaynes, Cavell, O Shaughnessy, Shields, Lear, S. Gardner, Korsgaard, P.M.S. Hacker, G.E.M. Anscombe
Views: 5

Views: 2
Campbells Pathways lecture from 1966
Views: 3

Video link
Views: 8

Views: 11

Views: 2
Freud
Campbell and Mythology Reviews
Paul Ricoeur Reviews

Views: 21
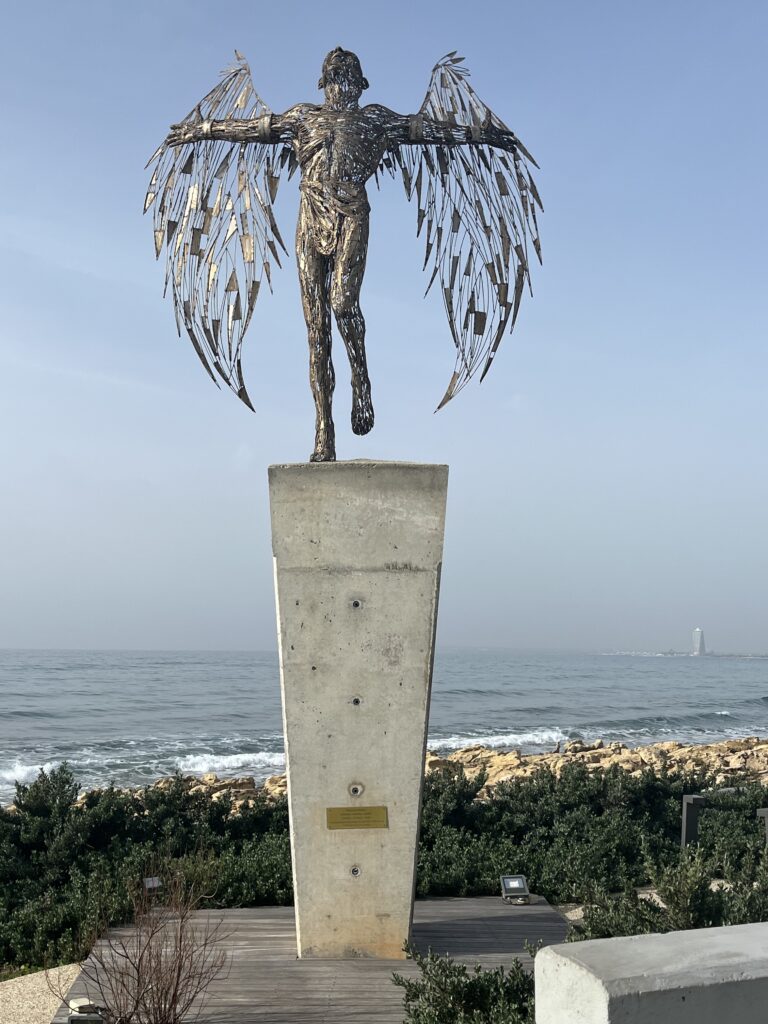

Wittgenstein claimed that the harmony between metaphysical entities such as thought and reality are to be found in the grammar of our language which also houses the essences of phenomenoal entities such as man which Aristotle defined as the “rational animal capable of discourse”. The legend of Icarus in Ancient Greek Mythology is of course a cautionary tale testifying to the consequences of the failure of rationality. Icarus was warned by his father not to fly too close to the sun which he did, thereby melting the wax that held the wings fastened to his body, thereupon plummeting to his death . This of course can not be a “realistic” phenomenal tale simply because we now know that constructed wings and wax do not have the energy to lift us high in the sky.
This tale, rather, had moral transcendental intentions that built upon a Kantian transcendental analogy which Kant defined in relation to our knowledge of God, thus:
“as the promotion of the welfare of children (=a) is to the love of parents (=b), so the welfare of the human species (=c) is to that unknown in God (=x) which we call love.” (Prolegomena to any Future Metaphysics”, trans Ellington J.W., Indianapolis, Hacket Publishing,1977, ftnt Page 98)
Paul Ricouer in his hermeneutical investigations of language, identified what he called the “realm of the sacred” which includes God and the reason he loves those humans who live holy lives, lives that, according to Kant, (who acknowledges this realm of the sacred) are led in accordance with the categorical imperative (treating all humans and higher forms of psuché as ends in themselves). The analogy Kant refers to above involves family relations which may also be in the realm of the sacred, if one reasons that children must be regarded as “known” ends-in themselves.
The love of God is an unknown end-in-itself, which some Freudians may regard as illusory, a wish fulfillment of gigantic cultural proportions. Kant has decided that this is not the case, and if our modern response to Deus Absconditis is a symbol worth interpreting, such an interpretation may result in the judgement that Kant was right in claiming that God is a necessary idea for the cultural development of human psuché: under the important condition, of course, that we “know ourselves”. Icarus was inebriated with the thought of the freedom of flying and refused to heed his fathers Aristotelian advice (The Principle of the Golden Mean). His fate was in accord with the Socratic idea of justice that people ought to get what they deserve in life. This legend was a family drama which was meant to be generalised to everyone in all moral circumstances.
Ricoeurs investigations of the realm of the sacred was conducted mostly as part of his into the “Symbolism of Evil” where he began by investigating the evil men confessed to. These confessions Ricoeur claimed were part of the process of “knowing oneself” , telling the truth about oneself. The nature of the evil is of course crucial to the future . Certain crimes such as murder for Socrates would result in a virtuous man being unable to live with what he had done, because it is now true that he is a murderer and it is impossible to live with a murderer.
We know Wittgenstein was a religious man and claimed to be more interested in aesthetic and religious problems. He, together with Ricoeur, was the most modern of the Philosophers, refusing to abandon certain traditions and regretting the passing of these traditions. The flying invention of Dedalus was a precursor to the invention of flight machines which would takes us around the world wherever we wanted to go. This invention in the name of freedom was of course to be used by the “new men” (Arendts term for those moderns filled with the hubris of Icarus) for the purposes of war and mass destruction which occurred whilst God was making an exit from our lives thanks to modern materialism and scepticism. God of course in a certain specific philosophical sense, lives on in the corridors of universities where Aristotelians, Kantians and Wittgensteinians found a refuge and a home. God lives on also in the pages of the writings of these Philosophers as long as we moderns can summon the energy to continue reading for the purposes of acquiring knowledge.
Views: 66

Campbell continues to discuss the issue of the rise of Islam in some detail noting that there is an assumption of the infallibility of the group or community (Page 436), and also that the Mind of the Community and the Mind of God are identical. To be clear, this is not in the Socratic spirit of seeking justice in the soul writ large (in the polis,) but rather something more radical, something more in line with Marxist Culture which denies the existence of the philosophical , transcendental and metaphysical realms, whilst simultaneously claiming a form of transcendence for the words of Marx-the prophet. Islamic poets/philosophers such as Mohammed Iqbal also expressed a criticism of Europe in the following words:
“Believe me, Europe today is the greatest hindrance in the way of mans ethcal achievement. The Muslim, on the other hand, is in possession of these ultimate ideas on the basis of a revelation, which, speaking from the inmost depths of life, internalises its own apparent externality……and in view of the basic idea of Islam, that there can be no further revelation binding on man.” (Pages 438-9)
We now know that for a number of Islamic societies there are radical conseqences for the freedom of the individual citizen of such Republics, but there are also consequences for an entire segment of the Islamic community, namely women, who are not treated equally in the spirit of European democracies. The birthplace of democracy, Ancient Greece, provided us with institutions and laws that grew naturally and organically from the lives of the citizens. These institutions and laws became part of the matrix from which both equality and freedom grow. The meanings of the terms arché, areté, diké, logos, psuché, aletheia,and epistemé were also critically interpreted in terms of many Aristotelian principles including the principle of the Golden Mean.
Campbell notes the challenges to Islamic logic from both the Shiítes and the Whirling Dervish Order. The former became prominent in the drama-filled attempts to find a successor for Mohammed after his death. Other significant events in the growth of the power of Islam included the shift of the Capital from Mecca to Baghdad, the city of pleasure, in 750AD, when the Umayyadi were removed from power. This period of Persian influence lasted until 1258 AD when the Mongols put the city to the sword brutally, allowing a resurgence of European influence.
Campbell discusses St Patrick of Ireland and his controversial contemporary Pelagius, who confronted the Church with the uncomfortable doctrine of the free will which probably had its origin in Ancient Greece, in particular, the work of “The Philosopher” of the period, Aristotle. This doctrine seriously questioned the thesis of Original Sin, which saw the will only in terms of the disobedience of Satan. The Neoplatonism of Erigena (815-877AD) was also condemned by Rome (Page 467).
The Celts, Cambell argues worshipped the mother of God, Mother Earth, and in the North the Vikings were roaming much of Europe and beyond, but especially harassing the Christians of Europe, embodying the hero-type of the warrior, at home in the killing-fields of war.
Pope Innocent III(1198-1215), the “greatest of the Popes, according to the Historians and Campbell, reinforced the opposition to Pelagianism and other heresies attributed to the Gnostics and Donatism. Pope Innocent himself became an object of suspicion but was never formally charged with any offence until he was moved by his own people into a state of retirement. In the context of this discussion, Campbell, referring to the avarice of the clergy, claimed:
“It is hardly to be wondered, then, why, in the course of the 12th century there should have developed throughout Europe a deep trend not merely of anti-clericalism but of radical heresy.”(Page 495)
Manichaeism, a form of Gnosticism, was also subject to the scrutiny of the Church authorities, and its leaders were burned at the stake. Campbell claims that these heresies were signs that European individuals had begun to think for themselves and cast off the yoke of the Church, refusing to believe in an “absolute Levantine consensus”. Anti-Papal polemics began to circulate and were promoted by various individuals, including Joachim of Flores, who appealed to many of the Fransciscan order who had postulated “The Age of the Holy Ghost” which involved amongst other things, a reduction in the role of the Church in everyday affairs. The Papacy entered a “time of troubles” when in 1377 there were suddenly two Popes because of a dispute between Italy and France, each excommunicating the other (Page 503), until the council of Pisa elected a third Pope. In the wake of these events John Huss (1373-1415) was burned at the stake for suggesting “Reforms of the Church”, thus preparing the way for Luther and the “Reformation”,one century later (Page 504)
Cambell has the following to say on the issue of the rise of the influence of the Europeans:
“In the broadest view of the history of world mythology, the chief creative development in the period of the waning Middle Ages and approaching Reformation was the use of the principle of individual conscience over ecclesiastical authority. This marked the beginning of the end of the reign of the priestly mind, first over European thought, and then as today, we see, in all the world.” (Page 504)
One could also characterise this period of European History in terms of a reawakening of the critical spirit and love of freedom that came down to us from the Ancient Greeks. This is a possible reading emanating from the History of world Philosophy. There would then be a possible continuous cultural thread leading to both the Renaissance and the Enlightenment. An Ancient non-European spiritual system based on revelation and miraculous happenings was never going to undermine the fundamental theoretical and practical rationalism of the Ancient Greeks. Rationality, moreover, could be widely communicated in a University system searching for the Truth, the Good, and the Beautiful, provided that the principle of specialistaion did not play the leading role in the organisation of university faculties. The University, then, was the institution best equipped to provide a life of eudaimonia, a life in which ruin and destruction could be overcome if ones knowledge was broad and deep enough and if one could also achieve the awesome task of “knowing” oneself.
Campbell also notes that a number of troubadours were connected with the Allbigensian heresy. These “popular” people spoke of Amor and the mystical rapture associated with such passion. This popular movement of course competed with the calm, collected contemplative life of the University, which appeared to concern itself more with matters of the soul than matters of the justice of the polis. Campbell notes,, however, the following:
“There is, in short, between the pagan past and High Middle Ages of Europe an impressive continuity of spirit and development. over which, for a time, the overlay of an Oriental type of spiritual despotism was heavily spread only to be disintegrated, assimlated and absorbed. In courtly and poetic circles the ideal of individual experience prevailed over that of the infallible authority of men whose character was supposed to be disregarded.” (Pages 509-510).
Such a state of affirs eventually resulted in three interesting European ages in Europe, Firstly, the Renaissance, secondly the Enlightenment and thirdly, the Romantic period in which even the authority of the rationality of the Classical and Enlightenment ages was questioned. We are now entering the “Modern Age” which, according to Arendt, began already with the Philosophers Hobbes and Descartes, who both in sceptical mood, raised doubts about the work of Aristotle which Kant attempted to dismantle in his critical Philosophy, only to have his own work partially dismantled by the “Spiritual” Philosophy of Hegel, which concluded with the Age of Romanticism that, in turn, detached us from our anchors in a stormy sea. The 20th century, according to Arendt was a “terrible century, with two world wars, the use of weapons of mass destruction upon civilian populations, a cold war, and the threat of mass-extinction hanging over us like a dark atomic cloud. All that is now needed is for a number of tyrannical “new men” to acquire power in power centres for this story of humanity to end mythologically instead of rationally.
Views: 65

“The Truth will set you free” are familiar words from the New Testament Bible (John 8:32) and they ought to be interpreted in the light of both what Christianity is, in its essence, namely a spiritual faith based movement and also in terms of what it did for the people who felt like slaves under the laws of their societies. So Truth and Faith can perhaps find each other in the spiritual rather than the academic domains, in the name of freedom.
Campbell, in a section entitled “The Age of the Great Beliefs” begins by examining the relations of the Levant and Europe, claiming,that “The Pantheon is the earliest of all Mosques”, a paradoxical claim that is not fully defended. The Greek Temple with its columns(inside and out) had no interior, whereas, Campbell argues, the Mosque appeared to be all interior, thus, on certain views, modelling the mind. Campbell also points out that :
“for Classical man the Temple of the Body”, too, had no interior”.(Page 397)
As if the organs of our body, including the brain, were not inside our Temple. He continues:
“The cognate views of the individual in this world is not that of an individual at all but of an organ or part of the great organism:—as in Paul or Augustine’s view of the Living Body of Christ.”(Page 398)
Aristotles view of parts and wholes requires that parts must in a sense be partially defined in terms of the characteristics of the whole they constitute, if we are dealing with living organisms such as human psuché. Aristotles view of psuché, therefore is that of a constellation of specific organs including that of the brain:—a constellation that allows Aristotle to define the essence of man in terms of the essence-specifying definition of “rational animal capable of discourse”. Aristotles definition assumes that what man does, is much more important to his Existence and Being, than what happens to him, because he is capable of knowledge informed choices that assume a will striving for the Good.
The relation of Aristotle to Levantine Culture is well documented and begins with al-Kindi in the ninth century, continues with al-Farabi, Avicenna, and Averoes. Avicenna in particular eleborated upon Aristotle in ways that were not completely in accord with the central tenets of hylomorphic theory. It was, however, clear from these Arabic translations and commentaries that Aristotle appeared more concerned with Logos in the sense of Logic, than Logos in the Christian sense of the Word of God. Averoes was perhaps the commentator that best represented the spirit of Aristotelian Philosophy , but what he claimed in relation to the soul or psuché did not appear to be Aristotelian.
Encyclopedia Britiannica on-line, reports that Jewish Aristotelianism developed through the medium of the Arabic language and spread to the regions of North Africa, Mesopotamia and Spain. All translations of this period, whether Latin or Arabic did not meet the high standards of current linguistic scholarship, which really began to emerge with the work of Robert Grosseteste. Adequate tanslations of the most influential works were, of course, of vital importance, once the first universities were established, partly because they could form an important platform for the communication of Aristotelian ideas to a broader audience.
The University system, however, as both Kant and Spengler have observed, followed a principle of specialisation which did not appreciate the universal intentions of Aristotelian Practical Science. Studying Aristotle at University, however, must have left no doubt in the students minds in relation to the problematic doctrines pertaining to “revelation-through-miraculous happenings”. Yet, there were countercurrents carrying us in the opposite direction, when the metaphysical writings of Aristote were characterised as “dangerous” in spite of the fact that in Aristotle,there was no anthropomorphised alternative figure, competing for the term “God”, merely an abstract theoretical entity he called “pure Form which had the power of thinking about thinking. Form is an Aristotelian term for “principle” and his work on Metaphysics is only about the search for “first principles”, a search which was deemed sufficiently “dangerous” to result in a Papal Bull being issued at Paris University in 1210: lectures were banned and Aristotles texts were burned.
Aquinas, however, was more sympathetic to Aristotle and stayed within the orbit of Aristotles ideas in most of his commentaries, but when it came to the soul of human psuché, Aquinas could do no other than follow the dogma of the church and insist upon the separation of the body and the soul: a position Aristotle would have objected to. Condemnations of heresy in 1270 and 1277 did not specifically cite Aristotle, but his views on Psuché or the soul were anathema to many Christian scholars. The organisation of the teaching faculties contributed to the tension over Aristotles ideas because certain faculties defined “Truth” in terms of “revelation” rather than in terms of the more rigorous Aristotelian logos based- account.
Aristotelian Hylomorphism, and his Philosophical Psychology, thanks largely to the Universities and their faculties of the Arts, survived until the Renaissance and thereafter emerged as authoritative in various contexts in the succeeding centuries: for example, via the works of William Harvey, Francis Bacon, and Charles Darwin.
During the 20th century a small group of university based scholars existed which could be regarded as Aristotelians and Kantians. During this period the Philosophy of Wittgenstein, especially the later retreat from logical atomism, to the more social view of language based on instinct, and embedded in the hurly burly forms of social life, was an important influence in neutralising both materialistic and dualistic accounts that were circulating in the name of empiricism and Cartesian rationalism.
Ancient Greek democratic ideas and governmental infrastructure, which included an independent legal apparatus that focussed on the unity of the citizens of the polis in a spirit of diké and areté, continued to play important roles in the progress of civilisations in Western and Northern Europe. Freedom or “Eleftheria” had, since the Kantian Enlightenment, become more and more important as time went by. Campbell quotes Spenglers view that there were also difficulties with the correct interpretation of the significance of the Magian Culture:
“The Magian Culture geographically and historically is the midmost of the group of higher Cultures:—the only one which, in point both of space and time, was in touch with practically all the others. The structure of its history as a whole in our world-picture depends, therefore, entirely on our recognising the true inner form which the outer molds distorted. Unhappily that is just what we do not yet know, thanks to theological and philological prepossessions, and even more to modern tendency of overspecialisation which has unreasonably subdivided Western Research into a number of spearate branches:–each distinguished from the others not merely by its materials and its methods, but by its very way of thinking:–and so prevented the big problem from being seen. In this instance the consequences of specialisations have been greater perhaps than in any other. The historians proper stayed within the domain of classical philology and made the Classical Language frontier their eastern horizon, hence they entirely failed to perceive the deep unity of development on both sides of their frontier, which spiritually had no existence. The result is a perspective of “Ancient”, “Medieval”and “Modern” history, ordered and defined by the use of the Greek and Latin languages. The Persian world fell to the student of Iranian philology….and so disappeared absolutely from the field of vision of Chistian Theology.” (Pages 399-400)
Spengler does not mention in this context the “Ancient Greek Philosophers” and the “Philosophical and Cultural Revolution” that found voice in the historical figures of Socrates, Plato, Aristotle etc. The issues of knowledge (epistemé) justice (diké) and freedom (eleftheria) were certainy neutralised in the process of “cultural overlay” that occurred with the Romans and their engineering/military language which translated many Greek terms such as aletheia(truth), psuché (soul/life) and edudaimonia (good spirited flourishing life) problematically.
What had been established via the work of the above three Great “Ancients” was an “academic psychical distance” to the object of study that has been the hallmark of University study ever since. One of the consequences of the collapse of this “objectivity” was to compromise the very idea of objectivity itself via a bipolar view of the terms “subjective-objective”, reducing the former to a psychological state of mind and the latter to the sensory apprehension and manipulation of material objects. Not even the Philosophy of Kant would be able to mitigate the effects of “subjectivising” many important regions of knowledge.
Heidegger, in his writings, pointed to this phenomenon, claiming that Western Culture had been “weakened” by what he called a “forgetfullness of being”, which he mistakenly attributed partly to Aristotle. The Romanisation of Greek Culture and the Latinisation of the Greek Language strengthened processes of “overspecialisation”, resulting in the Empiricism of Hobbes, Hume etc, and the dualism of Descartes that paradoxically rested on the material substrate of the brain. Kant stemmed the tide somewhat, but the faculty specialisation of Universities, quickly neutralised via Hegel, his Enlightenment attempt to restore the Philosophical heritage of Ancient Greece.
The Aristotelian formula for a unified and prosperous polis which referred to a large middle class formed by, and following, the principle of the golden mean, also demands a Greek-style governmental infrastructure This infrastructure fell apart perhaps during the reign of Alexander the Great, but definitely afterwards as Zoroastrianism and Christianity vied for cultural supremacy. Campbell cites the work of Professor R C Zaehner (“The Dawn and Twiight of Zorastrianism”) In which it is claimed that other cults were not given sufficient freedom to express themselves owing to a sociological principle which:
“only grows in force and terror as the violated coerced factions become increasingly intractable through the operation of a second law, namely that gods become demons;which is to say, that psychological and sociological factors neither assimilated nor recognised by the consciously controlled system become autonomous and must ultimately break the system apart.” Page 405
This is the bipolar phenomenon referred to earlier which tore the polis asunder. Without the democratic and Philosophical infrastructure of the Greeks, no sociological principle or law could prevent the polis splitting into fragments. This might even have been true of Alexander the Great’s Empire.
Campbell, in his sub-chapter, “Byzantium”, illustrates well the cultural similarities and differences between Ancient Greece and the Levant during the period up to the 6th century AD, when he notes that the Roman Emperor Justinian (who closed all the Philosophical Schools and Academies) was experiencing the same kind of problems which threatened the existence of the Sassanian Empire of Chosroes I (531-579). Both rulers believed in the sociological principle of Absolute Rule, rather than the Aristotelian Principle of the Golden Mean.
Campbell alsonotes that the key mythological/religious questions of the two Cultures differed significantly with Zoroastrianisms concern focussing on the relation between darkness and light and the problem of evil, whilst the concern of Christianity focussed upon the relatively abstract problem of the nature of Jesus’ Incarnation. It is certainly no exaggeration to claim that this question of Incarnation split the Church. This recalls another academic question, namely, whether the Kingdom of God was coming in the future, or whether the Kingdom existed as the Gnostics claimed, right here and now and within us..
For Aristotle Noos was the home of Logos which the Christians identified with the Word of God. If, then, the Kingdom of God was within, as many Christian determinists doubted, given the doctrine of the freedom of the will, there followed the problem of the possibility of refusing to heed the word of God. Both Aristotle and Kant believed that the freedom of the Will was the real determiner of ones life,and if this was the case, then knowledge (epistemé) of the future Kingdom to come would be relevant in this context only if, as Aristotle claims, the will aims at the Good in all human activity: a thesis that of course runs contrary to the doctrine of Original Sin. Both Aristotle and Kant, claimed that the good will was the fundamental condition of all ethical action that is in accordance with the categorical imperative which amongst other things demands that we treat each other as end-in-themselves.
Moving forward in History it was this categorical imperative that became one of the foundation stones of Human Rights, which became the focus of the United Nations, the institution Kant suggested at the end of the 1700’s. We can see, then, a line of continuity running from Ancient Greece, to the Renaissance, to the Enlightenment, to the formation of the United Nations. The concern for our individual spiritual development that we find in Mythology and Religion then, appears to be less relevant in the above secular context where the burning question seems rather to be, how to avoid repressing the desires and activities of those that wish to concern themselves with their spiritual lives. We seem to have inherited the Socratic approach to The Good in the soul, searching for it instead in the soul writ large, namely the polis.
Mary, the mother of Jesus was also drawn into the clerical dispute over the issue of incarnation: a dispute that Campbell notes spanned over 4 phases lasting hundreds of years. This timeline takes us to the rise of Islam which Campbell claims is a continuation of Zorastrianism, Judaism, and Christianity, mythologially speaking. Abraham, it is noted, was the common ancestor of both Judaism and Islam. Islam was a religion of both revelation and revolution. Mohammed was an illiterate prophet that claimed to have visions whilst meditating in a cave. In one revelation Mohammed is informed that it was the Lord who taught man to use the pen. Apparently Mohammed was pondering the mortality of man when a vision intruded, described by Campbell as follows:
“Its author was God, its subject man, Gods creature; and its instrument, the pen, the sanctified Book, which men were to read, study, recite and treasure in their souls.” Page 424)
This is a curious vision for a man who, tradition has it, could not read, but was nevertheless proclaimed by family and friends to be a chosen apostle. Very soon afterward Mohammed was calling upon priests in Mecca to eliminate all pagan images from places of worship such as the Kaaba. Both Allah and Yahweh were Gods of semitic desert communities. One crucial difference, as Campbell points out is that whilst Yahweh was a specifically ethnic divinity, Allah was proclaimed with universalistic intentions, turning to all Humanity with his messages. For, as Campbell claims,
“in Mohammeds day the Alexandrian vision of humanity had reached even the peoples of the desert.” (Page 433)
There was, as Campbell points out, however, a problem with the laws proposed by Mohammed. These so-called divinely inspired laws did not grow naturally out of a particular society at a particular period in time, but rather had its source in revelations and visions occurring to Mohammed in a trance-like state. Universalising these visions to include commuities living in deserts, in the mountains, coastal communities, and communities in the rest of the world, some perhaps with long common-law traditions, was always likely to meet with insurmountable difficulties. Communities with a long tradition of common law focussed upon a universal idea of justice that was founded on the free will, a critical spirit, and people getting what they deserved. The first and second of these factors of course, were not reflected in the revelations and visions of the prophet. The critical spirit in particular was accustomed to evaluating divinities in terms of philosophical partly secular criteria such as the Principle of the Golden Mean exercised in the spirit of psuché and eudaimonia (the good spirited flourishng life). Given the typical attitude of critical minds to phenomena such as revelations and visions, it is not surprising that Islam was not successful in recruiting such communities to their cause. Also, given the Islamic conviction that once instituted laws were immutable, this added another dimension of difficulty to the mission of broadening the horizons of the Islamic Religion.Campbell quotes Spengler on this issue:
“Whereas the Classical law was made by burghers on the basis of practical experience, the Arabian came from God, who manifested it through the intellect of chosen and enlightened men….the authoritativeness of Classical laws rests upon their success, that of the Arabian on the majesty of the name they bear.” (Page 435)
There is of course a difference between commuities with traditions of common law based on the precedents of individual judges in a well educated core of judges, and laws passed by rulers who may or may not have had the appropriate education and may or may not have the ability to recruit those who have had the appropriate experience and education. Recall also that Mohammad could not read and therefore was probably not familiar with the History of the World that was available to scholars at the time. The History of Philosophy and Science may also have been provincial given that Mohammed relied on an oral tradition of communication of ideas. Just these facts may also have limited both the content and form of the “visions” he experienced.
Spenglers “burghers” were not of course an infallible standard by which to measure the efficacy and virtue of laws but, depending upon the inherited humanistic/democratic infrastructure, these burghers may be a far more reliable source of justice and the good life, then the visions of an illiterate man meditating in a cave. These burghers were, given their obvious relation to Ancient Greek conceptions, also a more reliable source of justice and eudaimonia then many literate Christian scholars.
Views: 61

The Introduction to the Celtic Iron Age was mythological, a fact symbolised in the Arthurian legend of the sword being extracted from the mother-stone. Blacksmiths of this period were seen to be wizards/shamans possessing special powers. The time of the Celts was a time of druidic rituals, sacrifice in forest retreats, learning by rote a number of verses, and fantasy-laden belief in an after-life (“otherworld”). An example of the latter is given in a tale from Celtic mythology relating to a hero who is approached by a strange beautiful girl singing about the “otherland” over the seas and far away. They both sail away and the hero returns after what seems to him to have been a short period only to find that he has been away for hundreds of years and all the people he knew were dead. This is a 8th century tale from Ireland and we find similar romantic tales 4 centuries later connected to Arthurs Knights of the Round Table. Encyclopedia Britannica on-line claims that the word “Druid” means “knowing the oak tree”. Caesar is reported to have claimed that the Druids neither paid taxes nor engaged in manual labour. They were priests without temples . Caesars Gallic wars began circa 58BC and succeeded in limiting the power of the Celts who had been waging war in southern Europe. There were two centres of Celtic Culture, one in the Alps and one in Southern Germany during the early Iron Age. Campbell refers to the scholar Professor Mircea Eliade:
” a fascinating study of the rites and myths of the Iron Age has shown that a leading idea of this mythology was of the stone as a mother rock and the iron, the iron weapon as her child brought forth by the obstetric art of the forge. Compare the saviour Mithra born from a rock with a sword in his hand.”(Pgae 292)
Mithra was originally, one of the more important gods from the Persian Pantheon , equated by some scholars to the Ancient Greek demiurge. Encyclopedia Britannica on-line links Mithra with the Platonism of the Timaeus:
“As in the Timaeus, the human soul came down from heaven. It crossed the seven spheres of the planets, taking on their vices (e.g. those of Mars and Venus) and was finally caught within the body. The task of human life is to liberate ones divine part (the soul) from the shackles of the body and to reascend through the seven spheres to the eternal unchanging realm of the fixed stars. This ascent to the sky was prefigured by Mithra himself when he left the earth in the chariot of the sun-god.” (www.britannica.com/topic/Mithraism/Mythology-and-Theology)
We dont find such talk of the disembodied soul in Aristotle or Kant, both of whom would have seriously questioned the supernaturalistic content in the above mythological account: a supernaturalism that was so dear to the superstitious Roman mind. Campbell argues, concerning the History of the Celtic Culture, that:
“The earliest locus of the culture was Bohemia and South Germany, but it spread in its final century as far as to Spain, Brittany, Scandinavia and the British Isles, to furnish a base upon which the subsequent Celtic flowering of the La Téne period then appeared, circa 550-15 BC.” (Page 293)
This was the period in which the Celts besieged Roman territories and entered Asia Minor. In the early 4th century BC, the Celts crossed the English Channel. Julius Caesar in his work “Gallic War” described the Celts as follows:
“There are two classes of persons of definite account and dignity. As for the common folk, they are treated almost as slaves, venturing nothing of themselves, never taken into counsel. The greater part of them, oppressed as they are by debt, by the heavy weight of tribute, or by the wrongs of the more powerful, commit themselves in slavery to the nobler, who have, in fact the same right over them as masters over slaves. Of the two classes above mentioned, one consists of Druids, the other of Knights. The former are concerned with divine worship, the due performances of sacrifices, public and private, and the interpretation of ritual questions: a great number of young men gather about them for the sake of instruction and hold them in great honour.”(Pages 293-4)
Part of the attraction of the young that joined the Druid movement was exemption from military service, taxes and other liabilities. The Celtic Knights believed in the” lex talionis” form of justice : If a life was taken by someone that person ought to lose their life. Almost all the information we have relating to Celtic Culture comes down to us courtesy of secondary sources (Cicero, Pliny, Siculus) because Celtic cultural objects have not been preserved. Campbells points to the literature comparing mystical Druidic thought with Hinduism.
This romantic fairy-tale Culture peristed right up to the founding of Rome as is evidenced by the legend of Romulus and Remus being nurtured by a Wolf. Romulus we know from the legend eventually slew Remus and the city founded becomes Rome rather than Reme. The Romans developed a number of local sacred divinities. The home and the hearth became sacred, being associated as they were with both Vesta and Janus(the god of the door-threshold). Otherwise the Romans embraced the Greek Pantheon of Gods. Romans, like Plato, believed that the character of the soul was determined by the metal related to it. They believed a Golden Age and a Golden Rome would follow the Bronze and Iron Ages and their associated races. Virgil in his writings prophesied the coming of a wonderful Golden Boy which would signify the return of the Golden Age (Campbell Page 323).
The Roman Spirit was, of course, essentially a military spirit requiring faithful devotion to the Republic in contrast the Oriental spirit of dissociation from all worldly things (Page 328). And yet there is a belief in the afterlife in Cicero’s claim that warriors will have:
” a special place prepared for them in the heavens, where they may enjoy an eternal life of happiness” (Di re publica, Loeb Classical Library, Cmbridge, 1928, 6.13)
Campbell points out, however, that the tone of the Roman combination of duty and detachment is very different to that of the Orient. The implication of this is that the warrior knows hmself to be a God and this sets the stage for the veneration of the Roman Emperor as a God.(Campbell, Page 330). A parallel doctrine to this, namely the divine right of Kings to rule, was, of course a Christian based dogma used by a number of rulers throughout English History. The dogma often referred to the authority of the Bible which contrasts itself to the above Roman dogma based on Roman Mythology. The divine right of kings was never as closely associated with warrior-heros. The palaces of British Kings were never temples. This Roman doctrine may, of course have emboldened Pontius Pilate to give permission for the crucifixion of Jesus Christ. Both Roman Emperors and British Kings were in a certain sense miraculous beings but as Campbell points out on Page 344:
“If miracles are required India wins every time”.
Indeed what could be more miraculous than a universe created by a dreaming serpent. We, followers of Philosophy and Science dismiss miracles on good grounds with the resultant judgement “This is not the way in which the world works”. Campbell also helps to cast doubts on these miraculous claims when he points out that different mythologies produce different miracles, but the miracles of other mythologies are never recognised as genuine miracles, sometimes regarded as frauds, fabrications or witchcraft. The miracles associated with Christ, must, then be subject to doubt if we are to take New Testament accounts literally which we would seem required to do by the Christian Church. Later “interpretations” however rely on construing some of the books of the Bible as “literary texts”, and claim that the accounts of miracles must be taken metaphorically: intended to help unbelievers enter the realm of the sacred. Christ’s resurrection would seem in this context to be the most wondrous miracle. For the Philosopher, then, if the text relating to this event could not be taken literally then the only realistic alternative is to postulate that that the text is intended to be read metaphorically.
Paul, early on in Christianity, warned us not to be taken in by the “illusions” of Philosophy and perhaps he was thinking in particular of Gnostic challenges to many central teachings, but he may also have been referring to the authoritative influence of Aristotles principle based Hylomorphism. For a long period of history these Gnostic texts were not available to scholars for evaluation purposes. Relatively recently, however 48 works were discovered in an earthern jar near Nag Hammadi. Whether it was these texts which were the target of Pauls concern, or whether Paul was more concerned over powerful Aristotelian arguments against supernaturalism, is not known. The documents discovered contained reference to a doctrine of immantism which the Church for centuries had condemned: “The Kingdom of God is not coming, it is here”. Campbell believes immantism is well expressed in the following:
“I am the light that is above them all
I am the All
The All came forth from Me and the All attained to Me
Cleave a piece of wood, I am there
Lift up the stone, you will find me there.”(Campbell Page 367)
Campbell notes that the source of all of the material for the Gospels was:
“a common stock of sayings (logia) preserved and passed about, at first orally, among the communities of the faithful, which then become fixed in various ways in various writings.” (Campbell, Page 368)
The Gnostic position reminds one of the Aristotelian objection to the Platonic eternal Forms, which could not be found in the external physical world. The Gnostic Gospel of Thomas claims that the sacred Kingdom is not the Kingdom to come but rather that which is both here and now and within you. The Gospel of Thomas dates from circa 140AD which is approximately the time during which all the Gospels were being formed. The “authenticated Gospels of the Bible” were, Campbell, argues, fixed in Rome during the 4th century AD.
Campbell also refers to the Gospel of John in which God is praised thus:
“Glory to the Father!
Glory to thee, Word!
Glory to thee, Holy Spirit!” (Campbell Page 373)
This, Campbell argues cannot be the Father of either the OT or the NT but rather more closely resembles what we can find in Persian Myth, where the saviour “like Zoroaster descends from the sphere of Light; but unlike Zoroaster, partakes only apparently of the nature of the world”. (Page 373)
The Gospel of John characterises the crucifixion in unusual terms, thus:
“And in that cross of light there was one form and one appearance. And upon the cross I saw the Lord himself, and he had no shape, but only a voice: and a voice not such as was familiar to us, but one sweet and kind, and truly of God, saying to me: “John it is needful that there be one who hears these things from me, for I have need of one that will hear. This cross of light is sometimes called the Word by me for your sakes, sometimes Mind, sometimes Jesus, sometimes Christ, sometimes Door, sometimes Way, sometimes Bread, sometimes Seed, sometimes Resurrection, sometimes Son, sometimes Father, sometimes Spirit, sometimes Life, sometimes Truth, sometimes Faith, sometimes Grace. So it is for man. But what it is, in truth, as conceived in itself, as spoken between us, it is the marking off of all things, and the firm uplifting of all things, fixed, out of things unstable and the harmony of wisdom–of the wisdom that is harmony.” (Pages 373-4)
The contrasting of form and appearance , truth and appearance which God calls Word or Mind, does align with the Aristotelian position of Ancient Greece, especially if one considers the transition from Platonic to Aristotelian Philosophy which regards God as a Pure Form that thinks about thinking. For Aristotle, contra Plato, the forms are in the external world, which would seem to imply the thesis of immantism cited above by Campbell. Socrates in the Republic, we recall, praised the thesis of Anaxagoras that “All is Mind” which caused Socrates to completely change the emphasis of his philosophical investigations, from exploring the external world, to seeking Knowledge and Truth about the realm of Psuché.
Johns Gospel continues with:
“but what I am, I alone know, and no man else. Suffer me then to keep what is mine, but what is yours behold through me; and see me in mine essence, not as I have said I was but as you, being akin to me, know me.” (Page 375)
The text ends with John claiming to laugh at the multitude because, he held on to one thing in himself, namely:
“that the Lord carried out everything symbolically, for the conversion and salvation of man”
Symbolically? Metaphorically? We know the Gnostic view of the primacy of Knowledge was not shared by Pauls position that man is Justified by Faith alone. History apparantly has sided with Paul since his teaching appeared to have had the greatest mass-appeal. Paulianism claimed that Gnosticism fostered the multiplication of cults at the expense of the one true universal religion. Was this conversation between God and John something John hallucinated, or was it a metaphorical account of a thinking process that must have been a result of contradictions in the “sayings” witnessed by many different disciples and bystanders? The Aristotelian principles of noncontradiction and sufficient reason were part of the authority of his Philosophy at this time. Campbell, with considerable insight, sides with both Gnosticism and the Paulian Justification by Faith-thesis on the following grounds:
“Moreover, the paramount concern of a popular religion cannot be, and never has been “Truth” but the maintenance of a certain type of society, the inculcation in the young and refreshment in the old of an approved “system of sentiments” upon which the local institutions and government depend. And, as the documentation of our subject shows, the history of society itself has been marked over the milleniums by a gradual-ever so gradual—enlargement of group horizons: from the tribe or the village to the race or the nation, and beyond that, finally with Buddhism and Hellenism, to the all-embracing concept of humanity—which is, however, not a governable but a spiritual unit of individuals. And in such a unit there have to be many mansions, as there were in Gnosticism. (Page 378)
Wise words, indeed, but everything then hangs on how we construe Hellenism, whether in terms of a mythology or philosophy or alternatively in terms of the Aristotelian Golden Mean of Philosophical Mythology.
Views: 58

In Campbells opening to Chapter 6, entitled “Hellenism (331BC —324 AD”),he argues that:
“Greek Mythology declined from the status of religion to literature because of the highly critical Greek mind, which was already turned against it in the 6th and 5th centuries BC.” (Page 237)
This is an interesting and complex claim, perhaps resting on an assumption that religious texts were somehow differently structured than poetic or literary texts. There is one obvious difference relating to the events that are represented in these texts which in the case of poetry and literature might be known by the artist to be impossible in actuality, whereas in the case of certain fantastic Biblical representations we are expected to believe that these events actually occured when we know that as depicted they were impossible, given our knowledge of how the world is, and works. Religious texts are claiming actuality, reality (about real places, real people, real, events), whereas literary/poetic texts are merely claiming to be, at best, imitations of reality, laden with symbolic intention and referring to a latent content related to the aesthetic ideas of the artist.
The purposes of religious and literary texts certainly to some extent appear to be different. Adrian Stokes, the Kleinian Art Critic, compared Art and Love (Eros) in his essay on Michelangelo(The Critical Works of Adrian Stokes, Volume 3,London, Thames and Hudson, 1978), claiming that there is both an enveloping intention in Art as well as the singular idea of the essence of the object that is loved/appreciated. The art object, it is argued possesses a holistic self sufficiency which is embedded in the pulsing life of the world .The audience of literary performances often bring with them a wish to escape from the everyday life-world which Kant described as “melancholically haphazard”, containing as it does, violence, disease and many other forms of misery. The genius of the artist identifies with this spirit and uses this knowledge skillfully, in accordance with Kantian subjectively universal and necessary principles. In the middle of the constellation of such affects and effects, many have pointed out the resemblance of the appreciative state to the hypnotic state, which we know was of interest to Freud in the early days of psychoanalysis.
Now it is not out of the question that some religious texts aim at a similar hypnotic state in order to accomplish their mission of installing faith in the masses. Freud, refers to this process of envelopment as “the oceanic feeling”, claiming that it alone cannot account for our experiences of the sublimity of religious experience because of its initimate resemblance to the fantasy world of the imagination. The poet and the Philosopher have pedagogical intentions involving teaching the members of their audience something important about the world and themselves via in the former case the character and plot of the work. In the case of a Shakespearean play it is often the case that the 4 underlying questions(“What can we know?”, “What ought we to do?”, What can we hope for?”, “What is man?”, posed by Kant defines the domain of Philosophy and these are often featured as underlying themes of Shakespearean plays, conveyed via his aesthetic ideas. There is clearly, then, in both poetic texts and Shakespeare plays, both a manifest and a latent content constructed from these underlying aesthetic ideas. The Greek term Aletheia, (Unconcealment), which Heidegger claims was the Ancient Greek equivalent of Truth is also important in this aesthetic process of moving from the manifest to the latent content.
The key difference between religious and literary/aesthetic works is that the latter are not intended to be representations of actual events and people, and while they are not exactly fantasies of the kind we find in fairy-tales, they are nevertheless symbolic imitations of reality designed to refer via their manifest content to rational ideas of the good, true, beautiful, sublime, sacred, (latent content). Often poems or Shakespearean speeches have a “confessional” intention which hopes to reveal (aletheia) the state of the speakers soul/life.. One of the most important discoveries of Freud relates to the central agency of the Ego which he claimed was formed of the precipitate of lost objects. The losing of the the loved object demands at the very least a long mourning process with perhaps brief excursions into the psychoanalytic domain of the melancholic. The artis/genius knows this about himself and all other human beings and puts this truth to work in the organisation of his aesthetic ideas. In Shakespeares case we can also bear witness to the manifestation of other psychotic processes and defence mechanisms at work in furtherance of the plot of the work, for example, in Macbeths hallucination of a dagger and the ghost of Banquo, the man he killed earlier.
The world the artist is intent upon revealing the essence of, is not the melancholically haphazard world of everyday life but rather that world which contains a Kantian “hidden plan” for a hopeful future. This plan is not a utopian fantasy but rather the more down to earth hope that men in the future will treat each other with respect, in other words, treat each other as ends-in-themselves.
Religious texts are often about actions that occur “because of each other” and the correct understanding of their meaning necessitates an understanding of a complex non-linear idea of causation resembling the Aristotleian schema of fourfold causation. Ancient Greek Philosophy and Poetry both embraced the dualistic oracular proclamations:
“Everything created by man is destined for ruin and destruction”
and
“Know thyself!”
Both of these proclamations are causally related. It is necessary to know thyself if one is to minimise the human ruin and destruction that attend mans creations. This transcendental truth formed the background of Socratic, Platonic, Aristotelian, Kantian, and Wittgensteinian thought. Macbeths lack of self-knowledge, to take one example, led him to misinterpret the prophecy of the three sisters at the beginning of the play, thus leading to the desruction of both hmself and Lady Macebeth. These three sisters remind the classics student of the Ancient Greek Erinyes which were, together with Eros, replaced by the more temperate pantheon of divinities led by Zeus.
We ought to recall that oracular proclamations were received by their audience in a spirit of awe and wonder: their incantations, therefore, might have seemed hypnotic. More often than not these “messages from Apollo” (latent content) were delivered by females who claimed that the “sacred water spoke” (manifest content). It is reported that the Delphic Oracle , for example, often went into a trance-like state before delivering the incantatory proclamation. Whether or not this was a pretended state, or merely the posture needed for delivering incantatory proclamations, is not entirely clear. If the former was the case a Freudian explanation may explain why pretence was needed. The Oracle may be encouraging the natural learning mode of imitation in the audience , thus using the defence mechanism of identification. Perhaps poetry with its incantatory tone might have originated from this phenomenon, and thereafter inventively created other mechanisms to achieve its semi-hypnotic effects. The Poem, of course, is also a self sufficient object containing symbolic language and metaphors that are organised by aesthetic ideas and while not exactly sacred (a status claimed for religious texts), are certainly candidates for the status of the good, the beautiful and the sublime(a state intimately related to the human power of moral agency and the Good in General)
Cambell then claims that the critical mind of the Ancient Greeks pushed them to reject polytheism for monotheism which, of course, if true, would leave us with no option but to accept the thesis that we humans too, are self causing entities with a free will which, if used wrongly, results in evil. There is no reason to doubt that the Greek Philosophers believed that human willing was the issue behind the Oracles warning that “Everything created by man leads to ruin and destruction. Aristotle, we ought to recall in his essence specifying definition claimed that we are only “potentially” rational, and in practical contexts this means–under the condition of possessing a good will (which is the central issue of Kantian Ethics). Such a move to a conception of a will causing itself to choose or not to choose the Good necessitates a shift from the religious demand that we obey God, to the Philosophical demand that we understand what the divine Logos expects from us. Individual Responsibility thus supplamts faith in the Divine Being.
The fact that we possess such long childhoods (when compared to the animals) means that responsibility can only be expected fully from those that have left their childhoods and adolescence and are thereby free to exercise their rationality. This monotheistic conception with space for a self-causing free will was then overridden by the so-called Christian Truth, which Campbell expresses thus:
“The One God in three persons, with his pantheon of angels, counter pantheon of devils, communities of saints, forgiveness of sins, and resurrection of the Body, as well as the multiple presence of the dead and resurrected Son of God–true God and true Man—who was born miraculously of the Virgin Mother Mary.” Page 237
There are at least two supernatural events contained in this Campbellian version of the essence of Christianity—a life after death and a virgin birth, both of which would not have seemed realistic to Aristotle and other Greek Philosophers. By the time we get to Aristotle the Philosophical focus was on the universal and necessary characteristics of Being qua Being, a focus Campbell describes in terms of the Great Mother of the Pantheon and the different forms these pantheons took at different points in time. These different forms manifested the underlying power of her Being.
Campbell notes that it was Alexander the Great that put an end to the world order of divided kingdoms and Regions in the name of a universal idea/telos. Tutored by Aristotle, Alexander undoubtedly heard philosophers (perhaps even Aristotle) claiming that Greek ideas could rule the world. Alexander, in certain circumstances used Aristotles principle of the Golden Mean in his conquest of Persia, refusing to destroy the temples and shrines of conquered territories (thus refusing to follow the example of the Persians). The Persians may have been charitable to the Jews, but they did not extend this charity to the Greek territories they conquered. Campbell claims that Alexander created a new world order but in reality the principles he largely followed were both oracular and Philosophical. He announced to the Orient the substantial presence of a European spirit in the world. This new Spirit Camobell claims had 4 aspects: firstly:
“..we note not merely respect for the gods of all religions, but an almost scientific effort to recognise analogies: so the specific deities of the various lands began to be identified and worshipped as equivalent to each other” Page 240
Secondly, concerning the role of both Philosophy and Science in the interpretation of myth:-
“In the 6th and 5th century Greece, the philosophers had recognised a relationship of the Dionysian-Orphic complex to philosophical thought, and in the cults of the Orient they now discovered analogous possibilities.” (Page 241)
Thirdly,
“the breakthrough of the Greek inquiring intellect with Alexander into India, where a totally unforeseen species of philosophic inquiry had been developed in the various yogic schools of the Jain, Buddhist, and Brahmanic centers. A far deeper understanding of the practical psychological—as opposed to the cosmological—relevancy of mythology was represented in those disciplines, than anything the West was to achieve until the century of Nietzsche, Freud and Jung.” (Page 241)
Campbell also notes in this context that this practical psychological understanding included a good deal of what he called “psychosomatic mystic love”. Fourthly,
“after about two centuries of European influence upon Asia, the tide began to turn, until presently a powerful surge of reaction developed, which culiminated with the victories of Christianity over the gods and philosophies of Classical antiquity.” (Page 241)
Campbell eleborates upon this last point by claiming that the civilisation of the European West collapsed for seven centuries. There is much to unpack and clarify in the above 4 aspects but let us begin with the claim that we encountered a deeper understanding of the relation of practical Philosophy to Mythology in the Orient. It is not clear what Campbell means here. Freudian Psychology was Kantian to the core, and Kant certainly preceded Nietzsche, Freud and Jung. We have argued in earlier reviews of Campbells work that Kantian Philosophy and Philosophical Psychology does not contradict the often vague comments upon Being qua Being (Brahman?) we encounter in Hindu texts. We also noted that Kantian Philosophy is sympathetic to much that can be found in the Bible, but probably not to the postulation of events such as a virgin birth and resurrections. We pointed out that the insights Kant brought to the field of religion were very much influenced by Aristotelian Hylomorphic Philosophy. European History manifests a very clear line of development stretching from the Golden Age of Greece to the Art of the Renaissance, to the Enlightenment and Kant’s important contributions (and elaborations upon many different European ideas). There is also an imprtant Cosmopolitan thread linking Alexander the Great and Kants vision of a Cosmopolitan Kingdom of Ends. In other words the links between Kant and Freud to Ancient Greece were far stronger than the links to any Oriental conception of the relation of practical psychology to Mythology.
Insofar as Campbells fourth aspect is concerned, we also question the claim that Christianity triumphed over the Philosophies of Classical Antiquity. We are aware that all Philosophical schools were closed by Justine, a Roman Emperor, but this did not prevent Aristotle from being revered as “The Philosopher” throughout this period of so-called “collapse”. His influence upon both the European and Arabic World was considerable until the establishment of the First Universities when his influence was further sedimented in World-Philosophy and World-History. Indeed it is also important to point out that even Aquinas felt forced to confront and comment upon the works of Aristotle, translating the Greek into Latin in acknowledgment of “The master of those that know”. Aquinas claimed in Aristotelian spirit that all human life(psuché) is sacred because there is a spark of the divine within, and this certainly resembles the hylomorphic account of Noos. Yet there are tensions between these two thinkers on a number of issues including the notion of a free will undetermined by Gods natural and eternal law. It certainly appears to be problematic to project upon Aristotles Philosophy the Christian of Original Sin. Indeed, in this context, Campbell concludes with a remark on the Origin of Christian Mythology, claiming that it could be interpreted:
“as a development out of Old Testament Thought under Persian Influence, with nothing, as yet particularly Greek—unless the emphasis on love” (Page 290=
This confirms that European Culture was formed principally by journeys along two different roads: the roads leading from Athens and Jerusalem. Aquinas, then, can be admired for his attempt to reconcile these two very different accounts of man and his world, but in doing so he may well have diminished the importance of our Greek heritage which may well have pleased him. Fixating upon Love given the ambivalent nature of man does appear somewhat arbitrary, preparing the way for Romanticism and a “Modernist World.”
Views: 65

Campbell claims that Zoroastrianism has not left a great heritage possibly because of the :
“ravages of Alexandra the Great(331BC) and then, after painful reconstruction of the zealots of Islam.” (Page 201)
The Persian work, the Bundahish(“The Book of Creation”)was written between the years of 226-881AD, and the resultant creation contained both earlier and later content. The assumption of two primeval spirits, one better and one worse, is essentially dualistic and dialectical, leaving us with a bipolar attitude toward the Divine. In the context of this debate it also ought to be pointed out that Greek Mythology had its two Freudian Giants, namely Eros and Thanatos, working toward Ananke (fate), thereby essentially resolving a potential dialectical opposition with a Good telos. Greek Philosophy built upon this foundation by ackowledging a free will in relation to the concepts of areté(doing and saying the right thing in the right way at the right time) and diké(justice) both of which regulated by arché (principle).The matrix of Greek Mythology and Greek Philosophy provided the conditions necessary for the emergence of the Great Trio of Philosophers, Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, all of whom contributed to the creation of the meta-Discipline of Philosophy. The task of this discipline was to discover the myriad of principles associated with the Aristotelian Theoretical, Practical and Productive Sciences. Aristotle in his work “Metaphysics” (The study of First Principles) focussed on what he called “first Philosophy” which used the principles of noncontradiction and sufficient reason to explore the aporetic questions relating to Being qua Being..
There is in Persian Mythology, Campbell claims, a creative narrative relating to trees, animals and humans. Ahura Mazda, the Lord of the Light, upon seeing man said:
“You are Man, the ancestry of the world, created perfect in devotion. Perform the duties of the law, think good thoughts, speak good words, do good deeds and do not worship demons.” (Campbell, Page 205)
An antagonistic spirit caused the first two humans, who cannibalised their children, to quarrel but it is important to recognise that in this mythology, evil is conceived of as antecedent to the fall of Man, in direct contrast to the Biblical account in which a flaw in mans character is assumed, manifesting itself in disobedience in relation to the commandments of God. The Greek Philosophers thanks to thinkers like Anaxagoras, did not, like the Israeli prophets, see any relation betwee natural catastrophes such as volcanic explosions, floods or large meteor strikes and man-made catastrophes due to mans ill-will or ignorance. Anaxagoras, we recall, claimed that the moon, at the time conceved of as a divine entity, was constituted of material substance, and as such, had no influence upon the affairs of men. Campbell suggests that this problem of relating the conditions of the external world to the conditions of the human psuché, was not a serious problem for the Greeks, whose polytheistic pantheon could embrace all the nuances of physical and psychical existence. Believing in monotheism as the Jews and the Christians did, left them facing the problem of evil. Where did it originate? In God or in man? We know the choice was made to postulate that the being of man was fundamentally flawed.
The narrative of the Bundahish speaks of heaven, hell and resurrection in imaginatively dramatic terms, and also refers to a great meteor falling upon the earth, killing the serpent-divinity and purifying hell of its stench. Turning to man-made catastrophes, Cambell refers to the “strategies” of the Assyrian dynasty which included massacring entire populations or enslaving them. This occurred during the “Persian Period”(539-331 BC) which was largely a time for man-made ruin and destruction:
“Populations were being tossed from east the west, west to east, north to south and south to north, until, not a vestige of the earlier ground-in rooted sense of a national continuity remained.”(Page 214)
He elaborates upon the historical consequences for the period:
“The world-historical role of the Kings of Assyria can be described, therefore, as the erasure of the past and the creation of a thoroughly mixed, internationalised, interracialised Near Eastern Population that has remained essentially that ever since.” (Page 214)
It is fascinating to read about these tumultous upheavals, and the cosmopolitan consequences, as well as the total annihilation of the Assyrian Peoples. This pattern of annihilation and servitude was finally broken by Cyrus the Great, King of Kings, when a period of “restoration” began: a period that included restoring the people of Judah to Jerusalem. Cyrus restored Persian mastery of the region after overthrowing the Greeks. The Jews, in admiration, claimed that Yahweh himself spoke to Cyrus:
“I form light and create darkness, I make weal and create woe, I am Yahweh, who do all of these things.”(Campell, Page 216)
After a period of intensive warfare Darius ascended the throne to become the King of Kings, ruling from 521-486BC. It is said that in status he rivalled both Buddha(563-483BC) and Confucius(551-478 BC). Campbell points out that it was Oswald Spengler who claimed that the turmoil of this period was not caused by geographically situated nations but rather various sects and their churches:
“Such a group, as I have already said, is not a geographical nation but a church, a sect, the company in possession of a magical “treasure”;and the functioning of its treasure is conditioned by certain fairy-tale laws, which are the statutes of the group. Membership, therefore, is not a matter of either time or place, but of the knowledge and execution of the statutes, which are at once secular and religious, revealed, not invented by man; and categorical, not subject to review. When obeyed, they produce boons beyond anything the world has ever known—fairy-tale boons; however, when violated, even accidentally, they produce a magical catastrophe against which the force and will of the individual–or even of the now unfortunate group of which he is an organ–is as nought. Hence, finally, the weal and woe, virtue and value of all of each lie not in creative individual thought and effort, but in participation in the customs of the group: so that as far as the principle of free will is concerned, which is generally argued for in this culture, its effect is only to make the individual responsible for his decision either to obey or disobey. It is not his province to decide what is good and what bad.”(Page 223)
It is precisely at the inflection point of free will and responsibility that the Greeks saw the importance of knowledge (epistemé), and especially knowledge of oneself. Epistemé and arché form a synthesis which allow us insight into The Form of the Good and the Form of Truth (aletheia). For the Ancient Greek Philosopher, like Aristotle, the individual is embedded in his family constellation insofar as responsibilities are concerned, and to that extent, is not a completely free agent. The family can provide more than individuals without any social connection, but, as Socrates predicted, when groups grow large, desires multiply, desires which can only be fulfilled by being embedded in larger groups where responsibilities too increase in number. The Village is initially formed of a constellation of families and villages too can form the constellation of the polis. In such large constellations of people and institutions knowledge of areté (doing and saying the right thing in the right way at the right time) and diké (justice–getting what one deserves), become important values, and manifest powers of mind that are not confined to obeying a divinity or King of Kings. This knowledge embraced by the Greeks in relation to the goods of the body, the goods of the external world, and the goods of the soul, was not by any means an individual affair, but rather a universal and necessary endeavour resting on principles (arché). Here we need to undrstand what Socrates meant when he claimed that we need to search for justice and areté in the Polis, where the soul is writ large, and because of this fact requires a form of thinking that relates to the particular via universals and principles. Knowledge in this wider context, then, becomes the necessary condition of using ones will to achieve and appreciate the “Forms” of “The Good”, “The True” and “The Beautiful”. Eros, of course , was part of the Ancient Pantheon of Gods(Prior to the pantheon led by Zeus), forces and demiurges,and is present in all forms of life which, as Spinoza claims strives to maintain itself in its existence. Campbell claims that in the Greek Polis of Pericles, Eros becomes:
“the deity whose presence was the best support of law as well as life.” (Page 227)
This position, however, was specifically rejected by Diotima, the teacher of Socrates who we know so little about, and also by Socrates himself, as articulated in his speech in the dialogue, “The Symposium”. The Symposium pictures Eros with very human parents who conceive him during a drinking party. These parents are ,however, not individuals, but representative of the general characteristics of Poverty and Resourcefullness, and Eros is pictured as a poor figure padding barefoot through the streets of Athens in search of something not specifie,d but related to the desire each of us possesses, to find a soul-mate ( in Greek mythology both soul mates were united but split apart because of the fear of the gods that such a united entity would be too powerful)
This is a Freudian image of love in which once this soul mate has been found there is considerable fear that the soul-mate will be lost. Freud, in this context, charts the emotions of mourning and melancholia, locating the presence of the death instinct in the latter. Such imaginative narratives were of course sublimated by both Plato and Aristotle, who placed the “Forms”(principles) at the cente of Rationality, thereby replacing divinities with something law-like, that is a condition of all forms of activity (natural and human). In other words, love is not a God for the Philosophers, but rather a social means enabling man to overcome his natural anatagonism toward his neighbours and strangers, thereby facilitating communal forms of existence larger than the family. Love, therefore, may be more a function of mans “Spirit” than his rationality, which is in its turn connected to thought defined in terms of thinking about thinking, rather than our typically human form of thought which must think something about something. Freud points out in the context of this discussion, that marriage is the institution which formalises the end of our search for a soul-mate, but society places sometimes artificial regulations upon whom one may, or may not marry, thus causing a general sense of discontentment with ones civilisation.
The Bible contains passages claiming that God is Love and the two commandments of the New Testament are:
“Love God above all”
and
“Love thy neighbour as thyself”
If God is love, then Noos, that divine part of mans mind must also be a source of love, a source of The Good. Insofar as Kant and the Enlightenment were concerned, the first commandment requires more articulation, because, for Kant, it is the idea of freedom of the will that is a fundamental idea, perhaps more important than the idea of God, which Kant embraces strictly in accordance with his critical Philosophy, and not in the spirit of blind worship. Campbell quotes the speech of Agathon from the Symposium:
“all serve him of their own free will, and where there is love as well as obedience, there, as the laws which are the lords of the city, say, is justice.”
The Symposium too, had its Enlightened thinker, Socrates, present, questioning the premises of Agathons speech, attempting to make space for Platos Theory of Forms. Later, Aristotle would see in Eros the spirit that can give rise to excesses which the Principle of the Golden Mean is meant to regulate with the help of the human power of rationality. Aristotle, however, also refers to Eros in his work on Metaphysics as being involved in the motion of the cosmos that moves regularly, he claims, for the love of God, the unmoved mover. It appears, then, that thought and desire are fused into one in the Philosophical idea of God, but separated in huan psuché. Insofar as Eros is operating in the Instincts, it resembles Platonic Spirit, which can be difficult to control in human life. Control of the instincts, for Freud, requires various powers such as Consciousness, Repression, Identification, and Sublimation. Once under control we are presented, by Aristotle with a vicissitude of Eros, namely friendship, a milder, less impulsive, more rational, form of human relationship between men living in a polis. So Eros is not in itself a divinity but rather an important counterweight to the influence of Thanatos as well as a human power that requires integration with other powers of mind, for example, practical rationality in the form of areté, used by the Phronimos to provide laws for the polis.. The Will, solely influenced by Eros(the “melter of limbs”) is not free but rather, for Aristotle, Kant, and Freud, to some extent in servitude. In the Symposium, Eros is also associated with an original loss of ones “other half”, which motivates a sometimes lifelong search for the lost loved-half, thereby providing us with a melancholic view of what has been lost and its possible restoration. In such contexts, Freud speaks of the importance of the Agency of the Ego and the Reality Principle which assists us in a final acceptance of the loss of a loved object, in the spirit of discontentment. Such is the power of the pleasure-pain principle in the life of human psuché. Friendship, then, on Freudian theory may well involve the defence mechanisms of both identification and sublimation, resulting in the Aristotelian telos of treatng the friend as en end-in-itself, wishing everything for the friend that one wishes for oneself.
Sublimation is an important element of the learning process of creative artists: one in which instinctive impulses are sublimated in the process of the learning of ones Art. Campbell notes in this respect that Greek Art and Hindu Art differed in their derivations:
“Greek Art was derived from experiences of the eye; Hindu from those of the circulation of the blood.” (Page 229)
This Hindu preoccupation with inner processes would have been puzzling for the Greeks for whom the aesthetic journey began with the love of the beauty of the body, ascended to love of the beauties of the soul, and thence to the love of the beauty of the laws and institutions of the polis, culminating in a love for the beauty of every kind of knowledge which included a love for Philosophy. The experiences of the senses were, of course of singular importance for Greek artists, as is evidenced by their construction of beautiful temples and sculptures of Appollonian nudes. Campbell points to Hesiod’s Theogony in defence of his claim that Eros is the god of Love, and a member of the four original deities; the other three being Chaos, Gaea (mother earth) and Tartarus (the pit of hades). Hesiod clearly attributes the characteristic of immortality to Eros but also, paradoxically, a power that can overcome the rational powes of intelligence and planning. Campbell acknowledges that Eros does not appear in the writings of Homer because he belongs t the older pantheon of Greek deities. According to Hesiod, Eros is the son of Aphrodite but there are a number of different accounts of his parentage, including the anthromorphic account from the Symposium which claims that he was conceived at a drinking party by a father called Resourcefulness and a Mother called Poverty.
Campbell also claims that Greek Mythology distinguishes itself by a shift on the value-scale from the impersonal to the personal—the norms of the individual, he claims, were conceived to be more important than the norms of the group (Page 136). This claim, however, may ignore the extent to which the norms of the group were consciously and intentionally formed by the process of sublimating without repressing the norms of the individual. The common element of the norms of the individual and the norms of the group is arché, (principle), e.g. the freedom to live as one wishes on the condition that there is respect for others and ends-in-themselves. This would be part of essence of areté and diké, so important to Greek life.
Eros, if not a God, must, then, on the Philosophers view be some sort of principle that in the best case cooperates actively with the rational powers of human psuché, but it is the human pantheon of human rational powers that best assists in the building of the character of the individual in accordance with the universal criteria for “The Good.” Whether it is useful to characterise these matters as a move on the value scale from group norms to individual norms, is, of course, questionable.
Views: 70

In the Chapter entitled “Gods and Heroes of the European West”, Campbell provides us with his interpretation of the meanings of Homers Works, “The Iliad” and “The Odyssey”. He has the following to say about the Iliad:
“The patron God of the Iliad is Apollo, the god of the light world and of the excellence of heroes. Death, on the plane of vision of that work, is the end; there is nothing awesome, wondrous, or of power beyond the veil of death, but only twittering helpless shades. And the tragic sense of that work lies precisely in its deep joy of life’s beauty and excellence, the noble loveliness of fair women, the real worth of manly men, yet it recognises the terminal fact, thereby that the end is all ashes.” Page 162)
Campbell contrasts this with his interpretation of the tale of the Odyssey:
“In the Odyssey, on the other hand,, the patron God of Odysseus’s voyage is the trickster Hermes, who guides souls to the underworld, the patron also of rebirth, and the lord of the knowledges beyond death, which may be known to his initiates even in life. He is the god associated with the caduceus, the two serpents intertwined; and he is the male traditionally associated with the triad of goddesses of destiny—Aphrodite, Hera, and Athene—who, in the great legend caused the Trojan War.” (Page 162)
We know from Homers narrative that Odýsseus killed over 100 men during the course of his Odyssey. We also know, from other sources, that Hermes was the prodigy of Zeus and the nymphe Maia, the protector of journeymen, thieves and a guide for wandering dead souls. Recognised by his winged sanadals, hat, and staf,f and carrying the carvings of gods and two intertwined serpents. This staff was wielded by both Pythagoras and Cassandra, and reputedly contains the power of immortality for its owner. The Consciousness of Aletheia is reputed to have been embedded in the staff with memories of the secrets of Altantis, which were eventually divulged to Cassandra, partly through a hallucinated reincarnation. The Odyssey is a journey in search of Aletheia, the source of the mystery of humanity. Diké is only present in the form of lex talionis: “revenge, thyself!” Areté follows this latter divine imperative rather than its philosophical essence which demands the presence of the golden mean principles (arché) which guide one to do the right thing in the right way at the right time. The form of Aletheia is also modified by its intrenchment in the matrix of psuché, logos, epistemé, and eudaimonoa.
Prior to the philosophical revolution begun with Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, we experienced a democratic revolution began by Pericles, who perhaps set the stage for all political Philosophy in the future. Campbell quotes Pericles´ famous essence-specification of democracy:
“Our form of government does not enter into rivalry with the institution of others.”
The Persian Wars and the Peloponesian War were fought essentially over the democratic life style which athough wishing to live in peace with others, was nevertheless prepared to fight ferociously to defend a state where men obey the law and are otherwise free to live as they wish. This democratic legal state provided the stability necessary for leisure-time pursuits such as religion, poetry and Philosophy. Democratically inspired Athens then produced three of the Greatest Philosophers (Socrates, Plato, Aristotle) in a relatively short period of time (470BC to 322BC), all sharing that sanctified relation of teacher-pupil. Socrates was the teacher of Plato and Plato was the teacher of Aristotle. We would have to wait a myriad of centuries until the Renaissance for a reawakening of the slumbering Ancient Greek Spirit and its love of wisdom and freedom in all its theoretical, practical and productive forms. There is no doubt that Aristotles conviction that the forms (arché) are to be found in the external world if one knew how to think about this world. His grasp of the importance of experimentation (dissecting animals) and observation in relation to all formsof psuché laid the foundations for Darwinian biological science, Newtonian and Kantian Science, and Freudian Psychoanalysis. One can indeed argue that Aristotelian hylomorphism is largely assumed in the Philosophy of Kant which embraces both empirical realism and critical idealism. Kantian Critical Philosophy is a Philosphy of Freedom as an idea of Reason. Kant is not plagued by medieval theoretical difficulties of proving the existence of God, preferring as he did to postulate a practical reason to believe in God: a practical reason based on the premise of a good will striving to live a good spirited flourishing life.
Hylomorphism and Critical Philosphy is committed to the matrix of values which includes that of areté which Pericles embraced in his Political Philosophy:
“We do not copy our neighbours but are an example to them. It is true that we are called a democracy, for the administration is in the hands of the many and not of the few. But while the law secures equal justice to all alike in their private disputes, the claim of excellence is also recognised: and when a citizen is in any way distinguished, he is preferred to the public service, not as a matter of privilege but as the reward for merit. Neither is poverty a bar but a man may benefit his country whatever the obscurity of his condition. There is no exclusiveness in our public life, and in our private intercourse we are not suspicious of one another, nor agry with our neighbour, if he does what he likes…..In doing good, again, we are unlike others, we make our friends by conferring not by receiving favours. Now he who confers a favour is the firmer friend, because he would fain by kindness keep alive the memory of an obligation; but the recipient is colder in his feelings because he knows that he, in requiring anothers generosity, he will not be winning gratitude but only paying a debt. We do good to our neighbours not upon calculation of interest, but in the confidence of freedom and in a frank and fearless spirit.”(Thucydides: Pelopennessian War II, 37-40, Trans Jowert, B.,)
The Greeks, then, were very dissimilar to the Persian servants of the gods and self proclaimed tyrants. Campbell ponts out in this context that the Greeks were proud of having defeated the Persians four times and also of having found the best way for human psuché to live. (Page 179). One issue of importance for Democracy was the fact that during the era of Pericles and forward, only males could participate in affairs of state. Pericles, however rebuilt the agora and encouraged a number of poets playwrights and philosophers to fill Athens with their reflections. Thucydides claims that after the death of Pericles from the plague that devastated Athens, the generals and rulers thereafter made a chain of unfortunate bad decisions which eventually led to the loss of the Peloponessian War.
The Time of Pericles was a time for challenging absolute ideals and dogma,s whether they be theoretical or practical. Anaxagoras, a friend of Pericles, challenged the position that the sun and moon were divinities, claiming they were made of material substance following laws of the cosmos.He was exiled from Athens for his controversial views, but later Socrates would acknowledge an intellectual debt to Anaxogoras by giving up his investigations into the laws of the cosmos and “turning” to more abstract matters such as the True and the Good and the laws of the mind (human psuché) in accordance with the Noos-principle of Anaxagoras.
Aristotle, importantly differentiated further this view of the world by giving us an account of human psuché: a view which produced the essence-specifying definition of man as a “rational animal capable of discourse”. Anaxagoras continued the philosophical journey begun by Heraclitus and Parmenides, a journey that sought not to placate imagined diviities, but rather sought the Truth in the spirit of Aletheia, however uncomfortable the results of such philosophical investigations might be. Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle would also embark on these investigations, forming a unique trio of thinkers bound by a teacher-pupil relation: in marked contrast to the trio of Kant, Hegel, and Marx who sought to differentiate themselves from their predecessors. Kant was of course philosophising in the spirit of the Enlightenment which was inspired by the Spirit of Ancient Greece, both culturally and philosophically. Kant distinguished himself because of his historical insight and also because he provided us with an elaboration upon Aristotelian Hylomorphism which could then be used by Freud in the spirit of Anaxagoras. Neither Hegel nor Marx claim to be Enlightenment thinkers in the sense referred to above. Dialectical thinking, of course, has a history that takes us back to Heraclitus but dialectical reasoning leves us with major oppositions between science and Philosophy, Philosophy and Religion, Science and Art, etc which had previously been integrated in the thought of Aristotle and Kant in the spirit of Parmenides and Plato.
An important background influence on Ancient Greek Culture was that of the Orphic mythology that manifested itself in cultural rites as well as more spiritual activities such as song and lyre-playing which distracted believers from the more bloody activities of sacrifice. These more spiritual activities certainly influenced Pythagoras who, Campbell claims, was an Orphic follower as well as a thinker who believed that numbers could be heard in music, e.g. the ratios 2:1, 3:2, and 4:3. Pythagoras also believed that numbers are present in the “music of the spheres” and knowledge of these numbers was important to leading a satisfying life.
The Persian Prophet, Zoroaster is discussed in the Chapter entitled “Gods and Heroes of the Levant”. Oriental Mythology/Religion, Campbell claims, stands in contrast to Occidental mythology because in the case of the former:
“No attempt was ever made to bring into play in the religious field any principle of world reform or renovation.” (Page 190)
Zoroasters mythical Project builds upon the assumption that the world is not corrupt by design but rather had become so by a series of accidents connected to the activities of the human will. According to Zoroaster, what had been caused by the human will could be remedied by the human will under the condition of an engagement in the world which Oriental thnkers thought to be egoistic. Zoroasters teachings included appeals to the “archangels” of “Good Mind and Righteous Order” (Page 192). These “forces” engage with the powers of “Evil Mind and False Appearance”, e.g. Cowardice, Hypocrisy, Misery, and Extinction. Campbell claims that these beneficent and malevolent powers were subsequently transformed into the Christian orders of angels and devils. He argues that it is here where the ideas of free will and decision are born that would reemerge at different periods of clerical history. Such a position required too, a further appeal to a “day of judgement” in which these so-called “free actions and decisions” will be judged by the Will and Logos of the Divine Power. “Good Mind and Righteous Order” are related to thought, word and deed, and it is these that will be judged (P.196). These are the means which enable us to find our way to the Kingdom of the Divine along the “road of Zoroaster”. The evil, false form of life leads to a different destination, described as folllows:
“I saw the greedy jaws of hell; the most frightful pit, descending in a very narrow, fearful crevice and in darkness so murky that I was forced to feel my way, amid such a stench that all whose nose inhaled that air, struggled, staggered, and fell, and in such confinement that existence seemed impossible.”(Page 198)
We can see clearly here the work of the sensations, emotions and the imagination in contrast to the more abstract appeals to principles of Good we find in Greek Philosophy. The imagination has a bipolar capacity to picture conrete opposites. For the Aristotelian and Kantian Philosophers such bipolar alternatives are extremes which require the application of the principle of the Golden Mean or an account of human psuché embedded in the matrix of arché, areté, diké, aletheia, logos, epistemé, eros, thanatos, ananke, and eudaimonia. The above mythical operation of the imagination eleborated upon a vision of Arda Viraf: a vision that was adopted and transcribed and “more vividly described” by Dante (Page 199).
The above “visions” or “images” substantially influenced both Judaism and Christianity, and assisted by the emotions of fear and terror, contributed to limiting the more calm contemplative rational approaches to the realities experienced by the human form of psuché. Zoroaster may well have been a hero of the Levant but a prophet is not a Philosopher, and however wide his appeal may have been during his time, the day of this kind of hero were numbered. It was the Platonic account of the life and times of Socrates (including his death) that would introduce a new kind of hero onto the world-stage. Socrates believed in the examined life as did Plato, but it was Aristotles broad panoramic view of Philosophy and human psuché that settled the matter in favour of “The Philosopher”. It was this conceptually and rationally oriented “spirit” that inhabited the Philosophy of Kant during the time of the Enlightenment which preserved the influence of the Ancient Greeks upon our European Culture, that would remain relatively stable for the next 140 years until the First World War broke out. Hannah Arendt’s work “The Origins of Totalitarianism charts the “causes” of both the First and Second World Wars in a way that reminds one of the Platonic and Aristotelian opposition to tyrants, whose unnecessary and unlawful desires led to such ruin and destruction.
Views: 75

Campbell discusses the Yahwist chronicles relating to Abraham, and he notes the emphasis upon how ruin and disaster appears to follow those leaders who violate the divine commandments that have been named “the Law of Moses”. He concludes thus:
“Does it not, then, appear that we are dealing with the laws rather of myths, fairy tale and legend than any order of fact yet substantiated for either natural or human history? The Past, as in every other folk tradition of the world is here portrayed not with concern for what is known today as truth but to give a semblance of supernatural support to a certain social order and its system of belief…… All that is exceptional about the present remarkable examples is that, whereas no modern thinker in his right mind would argue for the historicity of myth brought together in the Odyssey, we have a modern literature of learning reaching from here to the moon and back doing that precisely for those sewn together in these ancient tales of about the same date.” (Page 125)
Campbell then elaborates upon this conclusion by referring to Freud’s 1939 Paper on “Moses and Monotheism”, in which, Freud, in accordance with the research of his time suggested not only that Moses was an Egyptian nobleman and not a Jew but also that he was slain during the Exodus. The conversion of the Israelites to Mosaic law, Campbell claims would actually take centuries before it was only temporarily instituted by the superstitious Josiah. The Freudian characterisation of this state of affairs was a diagnosis of neurosis, based upon a psychological explanation in accordance with his later theorising. Having murdered their leader, the guilt for this deed was passed down through several generations until another leader called Moses appeared on the scene. The mythology associated with Moses was, according to Freud, an imaginative screen memory constructed by using the defence mechanisms of repression, denial, displacement and idealisation to deal with the real anxiety that followed from the trauma associated with the cause and processes of the Exodus as well as certain post-Exodus events. For Freud, the origin of Jewish/Christian Religion must contain the element of the traumatic death of a beloved leader which in turn give rise to defensive dreamlike screen memories, to be distinguished, of course, from those accounts of events with purely historical intent. The events following the slaughter of the beloved leader resemble, for Freud, the influence of pathological guilt upon an ego weakened by various defence mechanisms, an ego fearing ruin and destruction and desiring supernatural protection from that ruin and destruction via various forms of wish-fulfillment. As a consequence, various acts of catharsis permeate the worship of such a being, but it nevertheless appears as if the historical truth of these events has eventually emerged.
Campbell introduces the logos of the Hero into this arena of discussion, claiming that “logic” demanded the transformation of Moses the Egyptian, into Moses the Jew. Apart from the difficulties with the mythological accounts of these events there are many other historical problems associated with the accounts of events we find in the Pentateuch, including that of the dating of the Exodus which was part of the “form” of the great cycle of the wandering of the patriarchs and their transformation into the “chosen people”(Campbell, Page 137). Perhaps it is, as Campbell suggests, that the real hero of this cycle was not Moses, but rather the emergence of Gods chosen people. The Jewish people thus become “symbols” for what is holy in what Paul Ricoeur called “the realm of the sacred”.
For Freud and Jung , the symbolism relating to the murdering of the father, undoubtedly had both a sexual and spiritual dimension ( a kind of resurrecting of the mother as goddess): the subsequent guilt being also associated with an attempt to convert the patriarchal social order to a matriarchal order. Kant, the Philosopher, spoke about a perfect moral/social order which was part of the “hidden plan” of civilisation: a process that he claimed could take one hundred thousand years.
The Philosophy of Ancient Greece and the Enlightenment Philosophy of Kant distance themselves from the dialectical problems associated with the resolution or synthesis of opposites under one representation. Logical principles such as noncontradiction and sufficient reason and practical principles such as “The Golden Mean”, begin from the perspective of the whole, and work their way down via the categories to parts which retain characteristics of the whole in the domains of “The Good”, “The True”, and “The Beautiful”. “The Holy” is, of course part of the “The Form of the Good”, along with “Justice”. All of these domains and realms are situated in a matrix of logos, phusis, aletheia, areté, arché, epistemé, psuché and eudaimonia: a matrix which finds the rational golden mean between dialectical extremes.
The concept of “The Whole” has also been the focus of Melanie Kleins Psychoanalytical theory. She relates the concept to that of the Whole Mother who has both Good and Bad aspects. She disagrees with Freud on the question of the dating of the superego in the process of psycho-sexual development, claiming that this aspect of the mind was formed much earlier than Freud suspected. Obviously the decentering power elucidated by Jean Piaget in which the individual child becomes able to see an object from a point of view other than their own, is a key factor in the process of the moral development of the child.
For Klein, the role of persecutory anxiety was related to the Freudian Death Instinct which seeks a return to inorganic (dead) forms, and was to be found in a wider range of phenomena than Freud specifically referred to. It could, Klein argued , be found in the relation of the infant to the mothers breast (a part object until the infant realises that the mothers whole permeates both her good and bad/frustrating aspects). On this account the power of the imagination of the infant is sufficiently well developed to engage in fantasising destroying the part object that is bad. In this process the breast is split into the good and the bad, the good being the breast that is the source of nourishment and safety and the bad breast being frustrating to such an exent that persecutory anxiety emerges as a consequence. Attacking the breast in fantasy is, Klein argues, a defence mechanism process, designed to protect the good breast from annihilation. This fantasy is the source of paranoid schizoid states that prevent an individual from seeing another human psuché as a whole, as something independently, good-in-itself.
The Human Psuché, Klein argues, moves from the paranoid-schizoid phase to a depressive phase because the individual begins a process of integrating their personality by uniting the good and bad aspects of the whole object under one representation, thus realising, for example, that it is one and the same mother, who loves, and frustrates, alternatively. It is at this inflection point that Eros makes its influence felt, becoming an important integrating force in the next stage of development: the depressive position/phase. It is in this latter phase that guilt begins to play a formative role as does the cathartic act of reparation. The depressive position has its own form of anxiety associated with it, namely,that connected with the loss of a loved or highly-valued object. In cases where regression occurs ( a weakened ego) there my supervene a state of melancholia in which the taking of ones own life may become an issue.
Mythology and Religion originate in this jungle of defence mechanisms and mental powers. To the extent that the defence mechanism of idealisation is involved, is the extent to which we encounter a primitive form of identification (another defence mechanism) which may lie behind the conception of many of our divinities. Greek Mythology it can be argued, avoided extreme forms of idealisation and may be more associated with the defence mechanism of sublimation than those primitive forms of identification involved in worship of many primitive objects.
In his Chapter entitled “Gods and Heros of the European West”, Campbell calls upon a Freudian analysis of the phenomenon of the displacement of matriarchal goddesses by Patriarchal warrior gods. There certainly was a manifestation of such displacement in Ancient Greece when Zeus is supposed to have given birth to Athene from his brain, thus also severing the previous integration of sexuality and spirituality which we find in goddess cultures. Had it not been for the presence of female oracles and the respect for their wise prophesies one may view such a phenomenon in isolation as the devaluation of the goddess culture:
“It is in fact amazing to what extent the female figure of epic, drama, and romance have been reduced to the status of mere objects;, or when functioning as subjects, initiating action of their own, have been depicted either as incarnate demons or mere allies of the masculine will……their accent is so displaced that they appear at first glance—though not, indeed, at second—to support the patriarchal notion of virtue, areté, which they actually, in some measure, refute.” Page 158
Even in Philosophical contexts during the time of Socrates we witnessed a diminshment of importance of female Philosophers like Diotima, one of the early tutors of Socrates. Many other female figures of wisdom throughout the ages with the possible exception of the oracles, have also experienced less attention for their wisdom. We know, however, that the oracle tradition in Ancient Greece lasted for approximately 600 years. For these oracles, epstemé was a major virtue. In speech, epistemé manifests itself in saying the right thing in the right way at the right time, whereas in action it manifests itself in doing the right thing in the right way at the right time. Arché, diké and aletheia also played important roles, especially in the Philosophies of the three Greats of the period, namely, Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, all of whom paid homage to the wisdom of the oracles, thereby elevating wisdom to one of the major themes of future Philosophy.
The Philosophers, we would argue, have therefore sublimated the goddess cultures that survived through the institution of the oracles, perhaps in a similar way to poets like Shakespeare. Insofar as the spirit of Philosophy and oracular wisdom inhabits certain quarters of our modern universities and modern cultures(poetry, religion, mythology, etc) these devalued female presences remain the latent content of our cultural dreams. Perhaps these Philosphers are also in some sense related to Tiresias, that figure who can be seen as a synthesis of the opposites of male and female.
Campbell paradoxically equates areté with patriarchal excellence in the above quote, perhaps because one of the principal virtues of Homeric Greece was that of Courage, given the fact that one of the major causes of the ruin and destruction of cities during this period was War. In such circumstances the physical prowess of men became a valued asset. There were however during various periods of the Ancient Greek era, female warriors who also manifested the virtue of courage. There is no doubt however, that insofar as the West was concerned the matriarchal culture slipped into the unconscious of our cultures, appearing periodically as “returns of the repressed”. Once this symbolic dream of displacement had achieved some cultural momentum these moments became fewer and fewer. Campbell manifests this problem in his account of “female excellence”:
“In this masculine dream world, the excellence of the female is supposed to reside in:
a)her beauty of form (Aphrodite)
b)her constancy and respect for the marriage bed (Hera)
c)her ability to inspire excellent males to excellent patriarchal deeds (Athene)”(Page 159)
Campbell also points out, in the context of this discussion, that Aphprodite was not above bribing Paris with the beautiful Helen, if he would only give her the golden apple she coveted. Recent evidence suggests that some of this myth of the fall of Troy may have credence. Campbell also evokes the Psychology of Jung who insists that however “conscious” we become of ourselves and our world, there will always remain substantial unconscious powers and ideas that will refuse to remain inert and buried and will in various ways seek expression through our encounters with others and the external world. Jung claims further that this transfer of unconscious energy will eventually transform x into its opposite, such is the lack of control we have over such forces and ideas.(Page 160)
Jung invokes Heraclitus who sees in the same road, both the road leading up and the road leading down. For Aristotle, however, the Logos of the road unifies these opposites and ensures that if we know that both of these aspects relate to the same road, we will not get lost in our journey through life. It is tempting here to invoke Freud and his Aristotelian and Kantian opposition to dialectical logic.
Homers Iliad and Odyssey are about events that are separated in time and many scholars have pondered what these two works say about the human mind. Julian Jaynes, the Princeton Psychologist, claims that the heros of the Ilaid, namely Achilles and Agamemnon are clearly not conscious individuals as we are but were subject to hallucinated voices that occurred when important anxiety related decisions were to be made. These individuals believed their voices to be of divine origin. Jaynes, however, questions the attribution to the divine, pointing out that all the sensory motor functions of the brain are bilaterally situated in both hemispheres, with the exception of Language, which, in the normal case, is situated in the left hemisphere. Jaynes also points out, however, that the right hemisphere is quite capable of recognising and even obeying elementary language forms and commands. Jaynes hypothesises that at a particular period in History, around 1200 BC, the transition to consciousness became a widespread phenomenon. Before this, In moments of high anxiety, he claimed, a voice which may have been the trace memory of the words of a wise man or supposed God would guide the individual to make the right decisions in life at critical moments. Kant, indeed, claimed that the idea of God was an idea in mans mind which has a very complicated relation to our mind and its knowledge of the external world. Kant believes that God is, in some sense a presence in our world, but one whose nature we cannot possibly fathom. This presence, however, will reward those individuals whose deeds are in accordance with areté, arche, diké, logos, epistemé etc. This may suggest that we cannot have any significant contact with God via our senses, but only through our wills which control our motor systems—on the condition of course that this will is both knowedgeable and wise.
Knowledge of the nature of death is also an important theme in Mythology and Philosophy and given that in mythology we are in the realm of the sensory–the image and its expression by the power of the imagination—such knowledge must remain limited and fail to reveal the extent of the presence of Thanatos either in the human psuché or in the world. The oracular proclamation during Ancient Greek Times to “know thyself!” must have challenged us to know something about the essence of death. Socrates in his death cell addressed this issue and the oracles must have been pleased by his account, thus confirming his status of being the wisest man in Athens.
Philosophically, the good whole object of the Mother was displaced not in favour of warrior patriarchs but rather “The Forms” (Principles) embedded in a matrix of physis, diké, areté, epistemé, logos, aletheia, techné, and eudaimonia. Plato summarised this state of affairs well in his dialogue, “The Republic” when he claimed that the form of the good was the highest of all forms, higher even than the Truth (aletheia). The sensori-motor world which was riddled with negations that naturally gave rise to a dialectical form of thought, was transcended in both the works of Plato and Aristotle. Kant, too, produced a Critical Philosophy that synthesised (resolved) a number of important dialectcal dilemmas in both his Theoretical and Practical Philosophy. Overall, one can claim that Philosophy in the above forms transcended mythical forms without volating the priciples of reason, categories of thought and concepts of psuché, areté, logos, aletheia, epistemé etc.
Views: 78

Zeus was undoubtedly a formidable warrior but he was also a compassionate God prepared to protect strangers. Just who might be an enemy and whom a stranger was probabaly decided on the basis of the character of the individual concerned. Zeus, we know, was also married to the goddes,s Hera, who, legend has it, blinded Tiresias for taking Zeus’s side in an argument about whether the male or the femal experienced more joy in the act of making love. Zeus could not undo his wifes curse but compensated Tiresias by bestowing upon him the gift of prophecy.
Sight is of course connected to the motor function of the will and it naturally introduces natural oppositions into the perceptual field. Having decided to travel up a particular hill leading to a particular professors house is riddled with negation. This hill versus that hill. This house versus all the other houses on the hill, and this Professor rather than the one that lives in the village. Over there is not here and here is not over there. Tiresias’s newly gained prophetic insight reached far beyond the visual arena of opposites and embraced the darkness of existence in itself. The voice must have dominated his oracular existence. All the oracles that followed Tiresias must have, to some extent, sought to imitate the state of this being, who had experienced being both a man and a woman.
In the division of the Universe following the famous victory of Zeus, Hades was given the earth where all the dead dwell; earth, the home of Gaia, the goddess of the earth and to the extent that Eve might have been related to Gaia(one of her daughters perhaps?), Eve becomes the OT mother of all life.Yet it was the warrior culture of death that prevailed over the more tranquill peaceful influence of female goddesses and oracles throughout the ages.
The Medieval Myth of King Arthur and his Round-Table Knights, in the spirit of the warrior went on Crusades determined to kill and conquer the non-believer, the non-Christian stranger (supported by texts from the Bible). Oppositions and negations ruled this era and Divine Commandments, and their sometimes peculiar interpretation, replaced appeal to the principles of everyday communal life. As far as the Ancient Greeks were concerned perception in the field of sensory-motor activity did not supercede the universal forms that appealed to the categories of understanding/judgement and the principles of reason (noncontradiction and sufficient reason). Indeed, for Plato, the sensory world was an inferior mode of Being compared to what was occurring in the realm of thought: a mode that imitated and merely “participated” in the world of thought and reason. For Aristotle, on the other hand, principles were to be found in the sensory-motor world if only one knew how to think and reason about this world.
Jean Piaget, the cognitive psychologist, designated the sensory motor domain as the primary focus for human beings from birth to two years old. Up until the age of 7 years the moral focus for the child was on the consequences of action, and the child at pre-operational stages, according to Piaget, was not capable of discerning intentions as being crucial to the question of whether an act was good and right or not. Once the child at 7 is able to grasp this concept of the Good, they can participate in grasping the principle of the good, which is both good in itself, and good in its consequences: a principle which is crucial for the ideas of duty and responsibility and of critical significance for maintaining order in large communities.
Returning to the example of the natural oppositions and negations we find in the sensory-motor world. If A was the Professors house on the hill and B was the students accommodation down in the village, the straight road leading from A to B could be joined by a straight line, and the distant opposites are thereby connected. For both the Professor and the student, their homes were the categorical centre for their lives, and the concept of “home” joined these seeming opposites into a unified representation which the understanding “thinks”.
In Greek Mythology, the goddesses Demeter, Persephone, and their foster son Triptolemos were jojntly responsible in different ways for the introduction of grain into human civilisation and this can be seen represented in a Mycenaeanean icon displaying Demeter handing a bushel of wheat to Triptolemos, who is holding a plough, making him thus one of the first divinities connected to techné (technology). Whether this is a divine symbol or an omen confirming the Greek oracles proclamation that:
“Everything created by humans is destined for ruin and destruction.”
will only be determined perhaps hundreds of thousands of years in the future. If the Oracle is correct, the icon will not be a symbol of life, but rather a symbol for death, ruin and destruction: the end of life, the end of the line from Birth (A) to Death (B). This line, then, AB, unites the opposites so poetically represented in the Christian Lamentation:
“Dust thou art, and to dust thou shallt return.”
For Philosophical thinking this line AB ends at B and cannot be extended further to C (the life after death), because the idea of another life after the telos of the end of life, is a contradiction and violates the principle of sufficient reason. The Socratic enigmatic appeal to Asclepius, as his death sentence was about to be executed, is typical of the sceptical Socrates (whom the oracle called the wisest man in all Athens), considering that Socrates believed that thisprophecy applied to him only because, unlike many others, he knew what he did not know, namely, that if there was some kind of spiritual continuance of his life, this could only occur in the mind of the Gods. For Socrates, this idea of the Gods was a given, which is clearly not the case for us moderns, who have been tutored by the logic of Science, Aristotle and Kant. For us the Gods are deus absconditis, and no longer play any role in our technologically costituted lives. The opposites of life and death for us humans are therefore well-represencted by our line AB, and also well expessed in the Christian lamentation referred to earlier.
Grain was a discovery of immense significance and it immediately led to the consequence of larger conglomerations of homes connected by many discoveries and ideas. As Socrates predicted in the Republic, when our communities grew, so did the repertoire of desires, both necessary and unnecessary, both lawful and unlawful. As more and more needs were being met in this large scale project of cooperation, other needs emerged in an uncontrolled manner. Aristotle begins his account of human psuché by characterising it both in terms of being a social animal, and as a rational animal capable of discourse. The former, of course, was an important condition of the latter, and it was these essence specifying characteristics that eventually led to the connurbation of the Polis, which required that strange form of human activity, namely, government.
The Ancient Greeks with their temperate relation to extremes, provided us with a blueprint for Democratic life which will stand forever. Kant put the matter well when he proclaimed man as a being who needs a master, but does not wish to be mastered by anyone else, thereby indicating that his potential for rationality would only be actualised in the far distant future (in one hundred thousand years).
For us, the tale of Gilgamesh, and his journey across the river of death to find “the plant of immortality at the bottom of the cosmic sea” (Page 91,) is as strange as the idea of a dead Socrates communing in heaven with the inhabitants of the “afterlife” in the realm of the Forms. The Gilgamesh tale ends with a serpent stealing the plant from Gilgamesh and becoming the cursed one, but simultaneously reviving the symbol of the Goddess. The tale of Gilgamesh does not resonate with us moderns, as much as it did, perhaps, in ancient times during the period prior to the Age of Heroes (1500-500BC) (Page 95).
Campbell argues insightfully, at the beginning of Chapter 3, that all the Origin Myths are in fact false, but there were also traditional books with historical intentions that could validate:
“the customs, systems of sentiments, and political aims of their respective local groups.”(Page 95)
But insofar these historcal intentions may also have been embedded in the poetic art, one cannot read these traditional books in the same way one does, our more modern History books. Such is the case with the OT. Moreover, some books of the OT have been rewritten over the ages, e.g. Exodus, Leviticus, Number, Deutoronomy and perhaps many others. This undoubtedly casts a shadow over the legitimacy of many books, and this shadow extends as far as the central figure of Moses (A fact Freud fixated upon in his work “Moses and Monotheism”). The Book of the Law of Moses, according to Campbell, came to light ca 621 BC in the reign of Josiah, and:
“no one had ever heard of this book of the Law of Moses and all had been worshipping false gods. Moreover, the God of Israel, now would punish them terribly–as he did indeed, within thirty-five years, when their holy-city was taken, its temple demolished, the people carried into exile, and another people put in their place.”(Page 97)
The above threat was reported to Josiah who purged the land of all idols, deposed idolatrous priests, destroyed houses of cult prostitution, destroyed the alter at Bethel, and removed mediums, wizards and shamans. Prior to 621 BC, the Law of Moses had been ignored by the Kings of many Cities and their peoples. Campbell notes, however, that the 4 Kings following Josiah did not subscribe to the Law of Moses. Moses, we ought to recall, called upon those following him to the promised land, to cast aside all graven images of animals, and embrace Yahweh’s written commandments as the only true articles of faith. That obviously did not happen, and it is uncomfortable facts such as this, which confirm Cambell’s scepticism concerning the perspectivalism of the worship of local divinities that have obviously been created by the imagination of man and then inflated into universal beings commanding the entire unverse.
Both Adam and Eve from the OT were cursed for their disobedience, but produced two children, Cain, the farmer, and Abel, the shepherd. The animal sacrificial offerings of Abel were more appreciated by Yahweh than Cain’s fruits of the soil, and in a fit of jealousy, Cain killed Abel, thus justifying the curse placed upon Adam. Cain was forced into exile to the land of Nod. These post-Eden events appeared to justify the expulsion of Adam and Eve from the Garden, and this sequence of events was also used to justify the thesis of Original Sin in the Garden, and the fallibility of man. The bipolar opposites of the Holy and Evil are obviously the driving forces of many Biblical narratives, and this is aided and abetted by the idea of the separation of the Creator from his Creation, which is a state of affairs we do not encounter in Ancient Greek Mythology. On the contrary, for the Ancient Greeks there is an innate human dignity in being human, a dignity that is to be respected by men and gods alike, and Creation is left to ancient forces such as the anonymous demiurge, thus preserving the realms of divinity and humanity under the Form of the principle of The Good.
In Oriental Mythologies and Religions, we and the divinities are separate aspects of the identical universal. We, and the divinities partake of being in spite of the fact that we are different forms of Being. The OT Yahweh, on the other hand, transcends all physical things and stands to living beings in the relation of being their separate creator. If A is Yahweh and B humanity, then no straight line connects these two forms of Being. We saw what fate befell Jesus for insisting that he is the son of God, for trying to draw a straight line between himself (A) and a God, point B.
The Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil are also separated entities in the OT narrative:
“whereas in other mythologies, both of Europe and the Orient, the Tree of Knowledge is itself the Tree of Immortal Life, and , moreover, still accessible to man.” (Page 106)
Campbell also points out the possible reason for the separation of entities these other mythologies regard as inseparable:
“our notion of religion is based on the recognition of a Creator distinct from his Creation, is fundamentally threatened by any recognition of divinity, not simply as present in the world but as inherent in its substance.” (Page 107)
Campbell elaborates upon this issue further:
“”A is not in any sense B. There can, therefore be no question, in either Jewish, Christian, or Islamic orthodoxy, of seeking God and finding God, either in the world or in oneself.”(Page 108)
Indeed, in our Christian religion, historically arguing that A is B, has been considered heretical, and perhaps typical of primitive religions of the primitive world. This absolute transcendence principle was also present in Platonic Philosophy, where the forms were also absolutely transcendent and enjoyed a different kind of existence to entities existing in the physical world. Aristotle, we know, disagreed with Plato on this issue, insisting that the forms could be found in the external world if one knew how to think and reason methodically. Spinoza carried this Aristotleian message further with his monistic account of Substance, and Kant further elaborated upon this Metaphysical view of Mind in relation to the laws of Morality.
There is one obvious danger in claiming that A is transcendentally identical with B, and that is the danger of narcissistically inflating ones worth to such an extent that one believes not as Aristotle did, that the divine dwells within our minds but rather “I am the divine”. Perhaps Freud’s patient Schreber displayed traces of such narcissism when he psychotically came to believe that his body was being diluted in the universe. Perhaps for ourTranscendent God, this form of Psychosis is the ultimate form of Original Sin that the Garden of Eden allegorises.
Views: 93

Final proofs sent away today. Published early next year
Views: 103

Miss Jane Ellis Harrison has the following to say on the theme of Western Heroic Mythology, contrasting it to underlying older mythological forms, which centre around the serpent and powerful cosmic forces:
“A worship of the power of fertility whch includes all plant and animal life is broad enough to be sound and healthy, but as mans attention centres more and more on his own humanity, such a worship is one divine source of danger and disease.”(Harrison, Themis, Cambridge, CUP,1927, Page 459.
Mythology, we have argued earlier, gave birth to a form of reflection and argumentation that abandons or sublimates the narrative plots of the deeds of warriors like Achilles, or prophets like Moses, in favour of the words of men who use their reason to understand and pass judgement on matters of universal importance for humanity. The introverted form of the narratives relating to Achilles and his forerunners and descendants do not, for Aristotle, connect with that part of the mind of human psuché he called noos, the part of the mind that he thought was intimately related to the divine. Physical courage as displayed by Achilles is, of course, important in particular environments involving war, but it is important to note that insofar as Achilles uses rationality at all (in his willingness to die for a perspectival cause), this use is instrumenta,l and locked onto aggressive self serving ends that the Greek oracles warned lead humanity down spiralling paths of ruin and destruction.
Ancient Greek Philosophy, but especially Socrates, Plato and Aristotle, provided us with some of the text to what Campbell refers to as “the deeper song” of ancient mythology sung by human psuché: a song that engages with the eternal silence of outer space and time in a spirit of worship. The song of the Philosophers, on the other hand, was neither a lamentation nor a joyous celebration of the human which, in their eyes, left a lot to be desired.
Classical Art, inspired by Philosophy, changes form from the Art that was inspired by Mythology, and contributed to singing this deeper song, especially during the period of the Renaissance where we saw a Greek holistic humanistic spirit and transcendence, revived in relation to the human psuche and linked in turn to the metaphysical realm of the sacred.
Campbell misses the philosophical deeper song and compares the song of ancient mythology with what he regards as the more superfical song of Western Mythology, which he claims is :
“something forced, and finally unconvincing about all the manly moral attitudes of the shining righteous deedsmen, whether of the Biblical or of the Greco-Roman schools.” (Page 25)
The deeper song of ancient non-Western mythology may be better represented by Kuli of India who is both life and death, womb and tomb of the world, and for whom the opposites of right and wrong, male and female were not absolute, where each opposite annihilates the other. Certainly the Greek Pantheon (inspiration for Western “balance of mind”), at least insofar as the earlier deities were concerned, did not seek ahhihilation of opposites, but rather engaged in the more balanced synthesising behaviour of, for example, having gods and goddesses marry each other , thus preserving the power of the mother earth representatives, rather than expelling them from the Pantheon. They were not cursed but regarded as ends-in-themselves, worthy of similar status and embraced in friendship. When they were the focus of sacrifices there was no dark intent lurking, namely, the hope that the transcendental divinity will depart and become deus absconditis.
The challenge that Campbells mythological reflections presents us with, is the challenge to synthesize the deeper song of mythology with the deeper song of Philosophy: this latter song is, of course, still in the process of composition, but one can clearly see in the initial movements of the composition, a kind of worship of the Truth and The Good. This is a very different proposition to that of worshipping individual heros, however powerful they may be.
Campbell discusses the Minoan Culture which we know, contained many goddesses and female cult leaders and it has therefore been classified as matriarchal in type. There were no walls around the cities and little evidence of weapons. The “atmosphere” of the culture is gentle with a commodious life-style in which social interaction extends broadly across class boundaries. The Minoan cults surrounding the goddesses could be both benign(involving cattle) and terrible (involving lions,) and central to these, was a tree of life and death, often associated with a Bull and the ritualistic practice of regicide. We referred earlier to Zeus and the primacy of the heavens over the sea (Poseidon), and the earth(Hades), which is also indexed in the developmental stages of the monument Stonehenge in England. The first Stonehenge monument consisted of sacrificial pits and an earth goddess cult, an evolutionary process ending with erect stones paying homage to the sky and solar divinities. Campbell claims that :
“The British dates match the Cretan perfectly.” (Page 67)
Contacts between Britain and the Mediterranean, the evidence suggests, occurred much earlier than previously thought. This was during the period when architects and poets were “wandering souls”, wandering from city to city, region to region and across various land-masses. Late Stonehenge may well have been created by a Mycenean architect. The Greek Pantheon, we know, began with Zeus, Poseidon and Hades dividing up the Universe between them: no female presences were involved directly in this process, and in spite of the Greek compromises with previous female divinities, earthly divinites gradually became occluded, as did their central symbol, the Tree of Life. As a consequence we see in the Garden of Eden Myth, that another tree, the tree of knowledge of good and evil begins to occupy the centre of concern for the deities. Knowledge, we know, also became a central concern for Philosophy: both knowledge of the external world and knowledge of the self.
Otto Rank, the psychoanalyst, was concerned with the psychology involved in the myth of the hero which, it is argued, resembles the structure of a neurotic naracisstic day dream:
“where the individual dissociates himself from his true parents by imagining for himself: 1. a noble or divine higher birth, 2. infant exile or exposure, 3. adoption by a family much more lowly than himself(namely, that of his actual parents), and 4. a prospect, ultimately, of return to his “true” estate with a wonderful humbling of those responsible for the exile, and a general sense of great achievement all around.” (Page 74)
The dissociation of oneself from the categorical relation we all have to our parents, and the categorical relation we also have to the world of sky-life, sea-life, and the life of the earth, uses the defence mechanisms of denial and splitting to alleviate a weak ego from anxiety and depression. Freud reports a case of psychotic dissociation, a case of paranoia in which the patient “(Shreber) feels that his own physical body is being dissolved into the infinite matter of the universe. Spinoza is in no doubt that we humans are an individual form of infinite substance intimately related to the substantial attributes of thought and extension. We strive to maintain ourselves in existence like all forms of substance, but inadequate ideas of our self, other selves and the universe hinder us from striving to fulfill our rational potential. Inadequate ideas, Spinoza argues, produce passive emotional states of mind that are not conducive to the classical Ancient Greek ideal of living a good-spirited flourishing life, a life of eudaimonia. Freud’s case, Schreber, is a more serious case of disssociation, more akin to the psychotic breakdown of the mind, than the neurotic accommodations the mind makes to a reality it is still in tenuous contact with. Campbell elaborates upon this theme:
“Indeed, it might be asked whether the morbid state of mind is not a function of the legend rather than its cause;for, as it stands, the beyond represents the descent from the cosmological plane to individual reference. It therefore, produces an inferior meditation, namely, instead of an extinction of ego in the image of a god(mythic identification) precisely the opposite: an exaltation of ego in the posture of a god (mythic inflation); which has been a chronic disease of rulers since the masters of the art of manipulating men contrived to play the role of incarnate god and yet save their necks from the double ax.”(Page 74)
Campbell argues that this state of affairs contributed to the transformation of the state/polis from a religious entity to a political entity. The human attribute of being a tyrant can be seen early on in History in the case of Hammurabi who likened himself to the sun that illuminates all the land and is charged with the duty of providing both justice and piety for his people. The sun sublimates the moon in this changing of the guard of the gods and fundamental differences of psychic attitude follow from such mythic transformation:
Whereas the aim of the earlier mythology has been to support a state of indifference to the modalities of time and identification with the inhabiting non-dual mystery of all Being, that of the new was just the opposite: to force action in the field of time, where subject and object are indeed two separate and not the same–as A is not B, as death is not life, virtue is not vice, and the slayer is not the slain.” (Page 78)
Thus, the womb of the narrative is about he who must overcome his opposite, the villain, or alternatively overcome a hostile world with strange and various life-forms in order to find peace of mind. The narrative is, then structured in accordance with a dialectical logic of thesis and antithesis, which in the best of all worlds, produces the synthesis, and names it as a kind of victory, instead of the more psychoanalytically tempered synthesis of a balanced rational adaptation to the hostile forces encountered. In its extreme form, when the image becomes more powerful than the word, images of a man walking on the surface of the moon is far more interesting than our mundane earthly journeys. This image of modern man is an image of an ego that must master the external world , the id, and the superego, whose Kantian task is to treat every other ego as an end-in-itself.
In the dramatic world of the hero there is no Greek synthesis of the opposites which is clearly not heroic enough for our Western Kings or Gods whose egos demand mastery, conquest, and victory for the drama to be complete. We can wonder whether such egos are also related to the Age of Adam and Eve who exercised their wills so positvely and dramatically in the sacred Garden. Such egos clearly no longer belong in the post Socratic world which is built on a categorical framework of epistemé, diké, arché, and areté (all forms of rationality). In this world, forms and principles constitute and regulate mans relation to his fellow man and the external world. For both Plato and Aristotle, the political sphere was not immune and it too, was constituted and regulated by the “Form of the Good”— a form that was both good-in-itself, and good-in-its-consequences: situated in a space that allowed the harmonious coexistence of the categorical universal ideas of justice, and the realm of the sacred.
The BiblicalCreation Myth relating to Yahweh was a late-stage patriarchal myth where the heros were “prophets and saviours”. The evolutionary development of the forms of creation-myth stretched, according to Campbell over 4 stages:
“1. The world born of a goddess without consort; 2. The world born of a goddess fecundated by a consort; 3. The world fashioned from the body of a goddess by a male-warrior god; and 4. The world created by the unaided power of a male God alone.” (Page 86)
The Bible is, of course, to the extent that it is a pre-historical, mythological document, but it is also an attempt to structure the time of this later phase of myth historically. Imaginative narrative is thus sublimated by historical narrative, charting the chronology of Kings and Prophets, as the figure of God successively recedes into the background to become Deus absconditis. The narrative of the life and teachings of the son of God, Jesus, becomes, then, an important focus and precedes the Age of the Holy Ghost to come, in which, on some accounts, the Church no longer needs to take the respnsibility for communicating the holy message that the Kingdom of Heaven is now, here on earth, and inside of everyone who will search for it.
This historical narrative record in its turn gives rise to the emergence of Ancient Greek Philosophy as well as the replacement of Myth and Religion by an overarching form of rational universal argumentation which could still find a role for the Holy or the realm of the sacred in the philosophical mansion of The Forms of the Good. Spinoza and Kant eleborated upon the Forms of Plato and the Hylomorphic Philosophy of Aristotle with firstly, a monistic ontological account of infinite substance, and secondly, a metaphysical dualism, namely, the Metaphysics of Nature, and the Metaphysicsof Morals. This latter domain involved the controversial practical idea of a being whose freedom consisted in an ability to cause itself to independently act and take responsibility for this action. 20th Century followers of Aristotle and Kant, such as Freud and Wittgenstein and their followers presented us with further elebaorations that can be added to the Canon of previous Philosophical works which, to some extent can be interpreted mythologically.
The question these two competing forms of account raise is whether both can be categorised as “the deeper song”: a song sung using the Philosophical faculties of sensibility(imagination), understanding, and reason.
“
Views: 99

We are all familiar with the proposition that perspectives can differ, whether that be in terms of attitudes toward some object, or in terms of the sensory conceptualisation of an object. What is, for one thinker, a rational animal capable of discourse, is for another thinker, the worst of the animals. In the former case, we obviously can share in the Logos that belongs to divinities, and in the latter case, the divinities might at best just abandon us (Deus absconditis) or in the worst case scenario, curse mankind for the rest of his days. Many of us have lived with this curse for millennia and some in modern times believe either that God is dead or that the divine has permanently absented itself from our lives.
Kant in his Metaphysics of Morals found a place for the divine and the realm of the sacred: a place in which the good will can become the holy will by, firstly, willing that ones maxims of action become universal law,s and secondly, by treating all human and divine psuché as ends-in-themselves. Following the threads of civilisation from the different regions of the Occident and the Orient, is a complex affair and testifies to the picture Aristotle painted many millennia ago, of the “Many Meanings of Being”.
Kantian Metaphysics of Mind elaborated upon the hylomorphic metaphysics of Aristotle by providing us with a relatively modern Philosophical Psychology capable of supporting the major concerns of thinkers throughout the following centuries. Kants theory assumes the essence-specifying definition of man as a “rational animal capable of discourse” in his divisions of the major faculties of mind into three: sensibility, understanding and reason. These faculties are capable of generating a number of cognitive and aesthetic powers, one of which was, of course, the imagination, which poets and religious thinkers alike, used in their various narratives of gods and goddesses, kings and queens.
One important thread leading from the Ancient Greek Philosophers, appeared during the periods of the Renaissance and Reformation, which in turn led to the Enlightenment and the emergence of the Kantian idea of the primacy of the will of man for the Metaphysics of Morals and the Primacy of the Being of God in the Metaphysics of Nature. Aristotle we recall, spoke of the role of noos in the context of the relation of human psuché to the realm of the sacred or the holy. Kant elaborates upon this by relating the noumenal self to the realm of the sacred or the holy.
Campbell, in his work, “Occidental Mythology”, points to the differences between Occidental and Oriental Mythology, in terms of topographic location, the enigma of transcendental experience, and the introverted and extraverted relation of man to the universe. He argues, paradoxically, that it is the Occidental self that is inward looking, and the Oriental Self that has an extraverted relation to Being. This difference may have been recorded in Freud’s judgement that our Western relation to religion is essentially pathological, reflecting the presence of infantile wishes and fears.
Kants relation to religion is, however, more sound, grounded as it was on the transcendental noumenal world that lay beyond all categories of thinking. Kant believes, like Aristotle, that self-knowledge is crucial to leading the examined contemplative life, but it was equally important to maintain a Philosophical relation to God if a good-spirited flourishing life was to be possible for the human forms of psuché possessing a good/holy will.
The Greek philosophical view of religion also focussed upon the ethical actions of human psuché, not as an individual causa sui, but rather as a necessarily social animal, ,which at their best, lived in a polis and democratically followed wise laws made by wise men. The Platonic dialogue “Euthyphro” testifies to this relation between justice and the sacred via the arguments of Socrates, namely, that the Just is a more embracing category than the sacred, and must, therefore, take precedence in the lives of man, the social animal. The role of rationality in this process was obvious, given the Socratic and Aristotelian claims that the best form of life was the examined or contemplative life, which, of course, presupposed rationality in its different practical, theoretical and productive forms. Knowledge of the Form of the Good was, for both Plato and Aristotle, the most important form of knowledge: a life based on knowledge was an examined contemplative life. It was this balanced relation to their world and themseves that allowed the more philosophically inclined Greek thinkers to sit in judgement on the character of the Gods and even question, as Socrates did, the primacy of the sacred over that of a form of reflection they called Philosophy, which Socrates named, in the course of his indictmen,t as one of the Children of the Gods. It did not, of course, end well for Socrates or Aristotle, but Plato managed somehow to avoid the persecution of the agents of religion. This challenge to religious authority was partly responsible for elevating abstract universal knowledge above concrete myth, which we know was not universal, but necessarly perspectival. One could not, for example, imagine Plato or Aristotle going to war with Socrates in relation to a difference in opinion over the “Form of the Good”. Individual heros or Gods and Goddesses, were being replaced, not by other heros, gods and goddesses, but by argumentation in accordance with logical principles and categorical conceptual distinctions. Freud would certainly have viewed the Ancient Greek Philosophy of Religion in terms of a healthy non pathological extraverted relation to the divine, free of hubris, infantile narcissism and its wishes and fears.
Both Spinoza and Kant argued for a Religion within the Bounds of Reason, insisting, for example, that reference to certain kinds of supernatural events in the Bible must not be interpreted literally but rather, metaphorically. The idea, for example, of a disembodied soul dwelling in a divine Kingdom of Heaven is, on such a view, a kind of Metaphor for the continued existence of the universal psuché.
Neither Aristotle nor Kant would deny therefore that although the enigma of Beings was difficult to decipher, the masks of these Beings did in fact reveal, for example, the presence of such Beings in Thought and in the extended world of Nature. Spinoza is the Philosopher that comes to mind in the context of this discussion, maintaining as he did that God or Substance has an infinite number of attributes, only two of which, namely, thought and extension, are accessible to mortal human psuché (an individual mode of Being). Kant, in his work, “The Critique of Judgement” referred to an inscription on a statue located at the Temple of Isis which claimed that no mortal had ever lifted the veil over the face of divine beings. This phenomenal account of the beings dwelling in the realm of the sacred comes to the attention of the individual mode of mortal human psuché via the attributes of thought and extension (only two of a possible infinity of attributes).
Now whilst Spinoza conceived of his Divine Substance in terms of the immanent cause of everything that occurs in the universe, his monistic ontology was questioned by Kant who conceived of a trinity of faculties of mind (sensibility, understanding, and reason) and a dualistic metaphysics of Nature and Morals, demanding different categorical frameworks to explain/justify natural events and moral actions. Spinoza invokes the notion of the knowledge of adequate ideas in a deterministic world-system, claimig that they play an important part in achieving amour intellectualis Dei–the joyous love of God, the infinite source of self-causing power in the universe, of which we, the human form of psuché, are a finite form, striving to maintain ourselves in existence using our finite power of reason and our inadequate and adequate ideas of the causes of our conscious experiences of the world.
Freedom for Spinoza, as it is for Kant is an idea of reason which uses its power to transcend inactive emotions and passions which are always based on inadequate ideas. It is not clear exactly, to what extent Kant agrees with this monistic ontological characterisation of God given his metaphysical dualism and his insistence upon a categorical framework of its own to characterise free human moral action, which, of course, presupposes knowledge of the operative causes of phenomenal events in the universe. Both Kant and Spinoza, however, are rationalists who are sceptical of religious texts promoting unrealistic desires and hopes and depicting supernatural events for which there could be no adequate ideas of the causes.
Kants Critical Philosophy, like the Philosophy of Spinoza allows us to conceive of the eternal in terms of its transcendence and immanence both here and now but also everywhere and for all time. Spinozas God is, of course, infinite and therefore beyond the here and now, whilst simultaneously being present here and now. God is also beyond but present in the true and the false , the right and the wrong. Critical Philosophy, however, prefers to view God as the moral guarantor for the good spirited flourishing lives of those worthy souls possessing good/holy wills. We have, Kant argues, more access to this infinite holy Being via our practical reason and our wills, than our theoretical judgements relating to Gods form of existence.
Aristotle, in his work on Metaphysics, chooses to conceive of God only through the attribute of Thought, yet transcending thought via the infinite power of thnking about thinking, whilst conceiving of the human form of psuché and its power of noos, to “participate” in this “first principle” or “form of the mind”.
Campbell claims that Art engages with both immanence and transcendence and various themes important to mythological thinking. For Kant, we know that Art engages aesthetically with life, and reference is made to the “form of finality” of the Art-object which the Art Critic, Adrian Stokes claims is a good object aiming to both envelop us in its constructed work, whilst simultaneously putting truth to work by standing transcendentally unconcealed for something good in life that gives rise to an intellectual pleasure that is perhaps related to the love one has for God via ones adequate ideas. Cambell expresses this by pointing to what he believes to be the metaphysical significance of art and its capacity to take us on a journey to:
“the shores of experience beyond the categories of thought.”(Page 3)
We appear on the above accounts to be in a realm beyond knowledge , a realm of Wisdom that incorporates both knowledge and the “form of the good” in accordance with different categorical frameworks. These categorical frameworks, for Kant, play a more decisive role, and have given birth to major criticisms of consequentialist ethical theories which invoke a theoretical linear cause-effect framework for the evaluation of what is good. Stating as these theories do, that it is good consequences that constitute the goodness of an ethical action, ignores the convoluted history of the opposition to this claim, which began by Glaucon demanding of Socrates’ theory of justice, that it be both, good-in-its-consequences, and good-in-itself. Plato produced his theory of Forms in The Republic, in response to this demand which helped to form the categorical framework for ought-statements (One ought to keep promises)–as opposed to is-statements describing a state of affairs. The modern rendition of the conflict between these categorical frameworks is the claim that one cannot derive an ought conclusion from a set of is-premises, on pain of being accused of the naturalistic fallacy. “Promises ought to be kept”, on this account, becomes a kind of justificatory principle: a constitutive condition governing the action of promising
Kant would refer to the “shore of experience” Campbel points to, in terms of a “feeling of life”, which can be described as a boundless outlook onto a future of happiness. This feeling of life is also accompanied by the pleasure at the harmony of the faculties of the imagination and understanding, which arises either firstly, because of the potential for the experience to be conceptualised in the case of the experience of the beautiful, or, secondly because of the potential for the experience of the sublime to associate itself with the moral idea of a moral agent possessing a moral will.
Art-objects created in the Greek spirit of areté (doing the right thing in the right way at the right time) and aletheia (truth being put to work in the object for the telos of unconcealment) are using the symbolic structure of transcendental analogy referred to by Kant in his work “Prolegomena”:
E.G., A is to B as C is to X
“For instance, as the promotion of the welfare of children (=a) as to the love of the parents (=b), so the welfare of the human species (=c) is to that unknown in God(=x). which we call love….But the relational concept in this case is mere category, viz., the concept of cause, which has nothing to do with sensibility.” (Page 98)
Another important form of the transcendental analogy occurs in relation to Art. Kant has the followng to say in a footnote:
“I may say that the causality of the Supreme Cause holds the same place with regard to the world that human reason does with regard to its works of art. Here the nature of the Supreme Cause itself remains unknownto me: I only compare its effects(the order of the world), which I know, and their conformity to reason to the effects of human reason, which I also know….”(Page 100)
The above is obviously a more complex structure than the use of metaphor we encounter in the poets use of this linguistic instrument, for example, in the expression “Man is a wolf” where human psuché is positioned in an epistemological structure of genus and species: thereby placing human psuché in the wider category of psuché as such and animal psuché in particular, perhaps simultaneously making the Aristotleian point that man can be the worst of animals.. Transcendental analogy, on the other hand, transports us further up the scale of rationality, to man at his best, striving via the power of noos toward possessing a divine sacred/holy will. It is in this region of Being that the Kantian idea of a boundless happy outlook onto the future, comes into play. as long as the outlook belongs to a man of moral worth and dignity. Kant’s vision is that the only viable practical argument for the existence of God is as a Supreme Cause of the “Kingdom of Ends”: an end state in which men treat each other as ends-in-themselves and as a conseqence rewarded with a good-spirited flourishing life (eudaimonia).
Campbell claims in this work that in occidental mythology the final terms God and Man stand opposed to one another, as contradictions, and therefore, pose a problem for the resolution of the problem of the opposition of the two contradictories. The Old Testament Book of Job demands absolute obedience to a jealous and angry Yahweh who chooses the tribe of the Israelites to be “his” people. Greek mythology, in contrast, prizes the judgement and dignity of man to such an extent that it is even capable of judging the character of the gods of the Greek Pantheon. The rational animal capable of discourse values his own form of human psuché almost as much as the form of God which he experiences via the proclamations of the prophets and holy men, who claim to have some kind of special access to the being behind the proclamations, or aternatively some kind of special access to, or use of, noos, the divine part of the mind of human psuché. Oriental Mythology, on the other hand, views this occidental perspective of Man as a possible equal and judge, at least insofar as his own life is concerned, as heretical, and the work of the devil.
We, in the West, communed with God in the Garden of Eden until the serpent and Eve colluded to persuade Adam to go in search for the Truth by eating the fruit from the tree of knowledge of good and evil, in contravention of the divine proclamation forbidding the act in question. The Serpent, Campbell claims, in Chapter One of hos work “Occidental Mythology” (New York, Viking Press, 2001, Page 9), was a divinity in the Levant for at least 7000 years before the book of Genesis. The Serpent symbolises death and rebirth and was a Lord of the Waters of the Earth whose activities are both constituted and regulated by the Moon. The serpent is, popularly speaking for modern men, a primitive form of life symbolising danger and the ruin of ones hopes. Previously, of course, the serpent was both a phallic symbol and a symbol for female genitalia, and we ought to recall in the context of this discussion, what whilst Buddha was sitting at the immovable spot beneath the tree of Enlightenment, he was approached in a threatening manner by Kama- Mara the creator of the world we think we know, and symbol of the desire for life and the fear of death, and it was Mother Earth who came to the rescue with the proclamation. “I bear you witness!”. This event was followed by Buddhas Enlightenment, whereupon a serpent enveloped the Enlightened one as a protective measure.
This is the Serpent the Old Testament Yahweh cursed upon learning of its role in the defiance of the divine proclamation. The female Eve, too, was cursed and the first couple were expelled from Eden and the promise of divine immortality was withdrawn, along with the company of God, who, at this point was well on his way to becoming a Deus Absconditis. The scene of the crime was the tree of the knowledge of good and evil, and this tree became the centre of a plot very different to that of Buddhas Tree of Enlightenment. This experience of Enlightenment for Buddha was a transcendental experience, transcending amongst other things the illusions of the world we think we know, which may well present as knowledge of the world and knowledge of human psuché.
Greek Mythology, however, had they imagined a Garden of Eden, would not have placed the first couple in such a state of subservience to the divinity of the Garden, and certainly would not have condemned the serpent and Eve for searching for the truth and placing the divine proclamation in brackets, whilst they satisfied their dpistemological curiosities. Campbell refers, in the context of this discussion to icons from the Near East, e.g. “The Garden of Immortality”, in which all the human figures are female (two of which are related to the underworld dvinity Gula-Bau, and one of which was a mortal woman grasping a branch of fruit:
“Thus we perceive that in this early mythic system of the nuclear Near East—in contrast to the latter, strictly patriarchical system of the Bible—divinity could be represented as well under feminine as under masculine form, the qualifying form itself being merely the mask of an ultimately unqualified principle, beyond, yet inhabiting all names and forms. Nor is there any sign of divine wrath or danger to be found in these seals. There is no theme of guilt connected wit the Garden.” (Page 13)
Campbell refers also to an inversion of sense in the legacy of Greek Mythology described by Jane Ellen Harrison in relation to the field-festivals and mystery cults. An earth goddess in various forms( e.g. the Erinyes?) reigned over the living and the dead:
“Her consort was typically a serpent form; and her rites were not characterised by the blithe spirit of manly athletic games, humanistic art, social enjoyment, feasting and theatre that the modern mind associates with Classical Greece, but were in spirit dark and full of dread. The offerings were not of cattle, gracefully garlanded, but of pigs and human beings, directed downward, not upward to the light: and rendered not in polished marble temples, radiant at the hour of rosy-fingered dawn, but in twilight groves and fields, over trenches through which the fresh blood poured into the bottomless abyss: “The beings worshipped”, Miss Harrison wrote, “were not rational human law abiding gods, but vague irrational, mainly malevolent spirit-things, ghosts and bogeys, and the like, not yet formulated and enclosed into god-head.” (Pages 17-18)
Campbell elaborates upon this theme by claiming that the spirit of the above sacrificial rituals was not that of giving in order to receive, but rather, of the giving of something in the hope that something unwanted will depart. Campbell also refers to the multifarious forms of the divinities by commenting on the icon “Zeus Meilichios”, expressing his amazement, given that this form originally belonged to a local daemon who was the son/husband of the Mother Earth Spirit(s). Such cults of fertility and sacrifice continued and became well documented by Sir James G Frazers work “The Golden Bough”. Frazer describes a sacred grove in which an ominous Priest-King roams with sword in hand ready to murder, perhaps setting the tone for Royal rule for centuries to come. In one Pre-Hellenic ritual scene from Epirus there is a sacred grove in which a maiden priestess without clothing brings swarms of snakes reputedly descended from the Python of Delphi, their food. How the snakes behave portends the spirit of the coming year, whether it will be fruitful and healthy, or riddled with disease and starvation. At the centre of this Greek idyll featuring a garden at peace, were women and serpents living harmoniously together. This idyll was disrupted by the nomadic Aryan cattle herders/warriors from the North and the Semitic sheep/goat herders/warriors from the South. These were people for whom “honour” was associated with prowess in battle and the conquest of desired territories.
Zeus, in fact, was a warrior God of this kind and his presence rapidly overshadowed that of the religiously inclined goddesses. Women, who were the givers and supporters of life were usurped by these new warrior-heros from the North ad South with their furious fires and swords. In the Old Testament this shift in the form of the divinity was characterised by Yahwehs slaying of the sea-serpet, Leviathan. The Greek equivalent of this symbol was the victory of Zeus over the younger child of Gaia, Typhon.
The Serpent symbol, we know, retained its hold over the Oriental Vedic Gods, thereby questioning the spirit of the warrior-hero which became the enduring symol of all occidental mythology: The Greeks, Romans, Germans and Celts. The slaying of monster serpents of the earth, celebrated the superiority of the Gods of the Heavens over the Goddesses of the Earth which were, over time, demoted to local daemons (Page 24)
The Garden of Eden Myth is clearly not as ancient as the monster/serpent myth, and is perhaps interpreted too anthropomorphically. The serpent that could talk was certainly a divinity, as must have been both the characters of Adam and Eve, even if here too Adam was the superior being, giving up a rib for the creation of Eve. Both of these characters, living as they did in the Garden, had access to the Tree of Immortality. The plot of Eve tempting Adam with earthly desires and subsequent exile from Paradise along with the serpent did not set out to praise the character of man, as might an Aristotleian-Kantian reinterpretation of these events. The Philosophical perspective would not focus upon the sin or flaw of mankind, but rather upon the act of will by both Adam and Eve to freely acquire knowledge from this mysterious Tree.
The Tale of the Old Testament is, of course, designed to warn all of mankind of the possible ruin and destruction that might follow from mans hubris, from turning ones back on ones God, but if, it is the case, as both Aristotle and Kant claim, that human psuché can only experience God via noos, the divine part of their minds, then the human psuché also becomes a causa sui, a cause of its own potential for Being rational and approaching the divine form of Being. For these Philosophers, the Garden of Eden myth becomes a celebration of the moment man freely chose the human form of life.
Views: 113

The Romantic commitment to viewing man as an individual whose fundamental interest is in using instrumental foms of reasoning to survive and provide himself with Hobbesian commodious forms of life in accordance with a social contract with the state, is, of course, an anti-Enlightenment position. Yet Romanticism is, as Campbell claims,an important elemental component in our Western Traditions. T S Eliot’s “modernist” perspective on the consequences of this tradition involves characterising the state of the modern world in terms of a Wasteland”:– a land in which people lead inauthentic lives.
Campbell notes in an interview entitled “The Meeting with the Goddess” ( “The Heros Journey), how Christianity was assimilated in Europe during the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries. In elaborating upon this theme, he notes that the bishop/abbot, Joachim of Florence, characterised the Christian Spirit in terms of “Three Ages”: The Age of the Father(Judaism), The Age of the son and the Church spreading the good news to the world, and the final Age of the Holy Spirit which dawned in the 15th century, and in which the Spirit has no need of the church, because the spirit will be directly teachable. This view was regarded by the Church as heretical but according to Campbell this is the view that is embraced by the Grand Romances and stories about the Knights of Arthurs Round Table, which mark a significant deviation from the Christian doctrines preached by the Church.
Given the history of what can only be described as the relative collapse of the role of the Church in our communities, and the subsequent wave of secularisation in the West (which may or may not retain the memory of the teachings of Christ and the Holy Spirit), it is hardly surprising that the consequences of these processes bore the poisoned fruit of the 20th century:—the century of the wasteland which Arendt described as “this terrible century”. Some psychoanalysts took the view that man was in need of treatment for his unnecessary desires and fantasies, and that the balance of mind of man had been significantly disturbed.
In an interview entitled “The Magic Flight” contained in the work “The Hero’s Journey”, Campbell is asked about his pilgrimage to Japan and, and he responded with the observation that the whole society seemed comfortably structured. He also points to the continuity of Art and Nature, and a union of the spiritual with the physical, which is a part of the Zen idea that all the things in the universe are part of a greater universal consciousness. Contained in this idea, Campbell argues, is the recognition that the separation of individual consciousnesses is a result of the organisation of our spatial- temporal experiences. On this view, reference to the particular historial events of Buddhism are of secondary importance to the general significance of Buddhist wisdom. Campbell points out this is not the case with Christian religion. If, for example one questions whether the Exodus actually took place, or whether the resurrection of Jesus actually occurred, this form of questioning suffices to call the whole tradition into question. Philosophically, of course, it is far easier to believe in the phenomenon of the Exodus than that of a physical human being genuinely dying and returning to life. Campbell notes in relation to this discussion that a particular historical perspective may well conceive of the impossibility of the end of time but this is psychologically irrelevant to the believer. In his view what is important to the believer is:
“When you have seen the radiance of eternity through all the forms of time and it is a function of art to make that visible to you, then you have really ended life in the world as it is lived by those who think only in historical terms.” (Page 185, The Hero’s Journey).
Campbell claims interestingly that the “Christ and Buddha ideas are perfectly equivalent mythological symbols” (Page 185). We in the West, however, in contrast to our Buddhist and Japanese friends, have lost the capacity to “Live in accord with nature”. Campbell responds to this point by reference to Biological science and a film of raw protoplasm under a microscope flowing this way and that, changing shape. Campbells interviewer puts the following question:
“So you think at the protoplasmic level there is some intention?”
Campbell replies:
“There has to be!”
He adds that the physicists of his time are claiming that energy and consciousness are two aspects of the same thing, which is certainly in accordance with the Kantian distinction of the phenomenal and the noumenal. Campbell elaborates further upon this vision:
“Let us say that every organ of the body has its energy impulse, an impulse to action, and the experience of the different conflicts of these energies is what constitutes the psyche.”(Pages 187-188)
One could also add here that the harmony of these energies in the collective action of several organs, is also an important part of the human psuché. Kant, the transcendental philosopher, par excellence, was called by critics, the great destroyer of metaphysics, but his works in fact are a testament to the idea of transcendence we find especially in the Oriental Mythologies.
Campbell claims that “Mythological images are transparent to transcendence” (Page 197) and this is confirmed in his constant references to the Gnostic Gospel of Thomas, where it is proclaimed:
“The Kingdom of the Father is spread upon the earth and men do not see it.”(Page 197)
This Gospel also states that the Kingdom is within you, making sense of that ancient Greek oracular challenge to “know thyself!”. The wave of secularisation in the West has ensured a focus on the science of sociology at the expense of Biological science and the hylomorphic Philosophy of Aristotle and Kant, and the unsurprising consequence of this has been diminished attention to the concerns of both mythology and Philosophy.
Campbell, like Piaget, believes in Lamarkian ideas rather than the “mechanical ” view of Darwin which appears to eschew the concept of the telos of life or its intention. Aristotle, we recall, argued that psychic life cannot be completely characterised without reference to its final cause, which compliments references to the material, efficient and formal causes. Campbell refers to the Myth relating to the tree of life in the Garden of Eden from which humanity has been exiled because of the sin of eating the fruit of the tree of the knowledge of good and evil. Jesus we know was crucified on the wood of this tree. Here we are provided with a dual message about life: firstly that phenomenal life is temporal(where the final cause is the end of life (psuché) and,secondly, the noumenal eternal, immortal life, something which we however can only understand from the present here and now-perspective.
In spite of several references to the Philosophy of Kant there is no reference to the moral and political ideas of Kant, including the moral telos for humanity referred to as the “Kingdom of Ends”. This telos or final cause answers the Kantian aporetic Philosophical question posed for the whole of humanity, namely “What can we hope for?”. The answer Kant offers, is that we ought, categorically, to treat each other as ends rather than as means to ends and this in turn requires of responding to the oracular proclamation to “know thyself!” and perhaps also to the Hindu message “Thou art that!”. Kants hopeful message is, however, also tinged with a melancholic lament over mans tendency not to know of himself that he is a being that is in need of a master but whose narcissism rejects the leadership of others.
Campbell is very critical of purely historical accounts of the lives or prophets and saviours on the following grounds:
“The Buddha lived from 563 to 483 BC. The first life of Buddha was written in 80 BC in Ceylon. We dont know anything about Buddha. We dont know anything about Christ. We dont know anything about Zoroaster. All we know are the legends of what the meaning of their lives is”(Hero’s Journey, Page 205)
If, as Cambell maintains, Art is the interpreter of Myth then the Great period of the Renaissance ought to be studied more closely from this point of view. Campbell provides us with a starting point:
“What happened in the Renaissance is facinating, Cosimo de Medici received a manuscript from Macedonia that was brought by a Greek Monk. It was a manuscript of the Corpus Hermeticum, which was a body of late classical text about the symbology of the classical world, which was exactly contemporary with the formative period of Christianity the first two centurues.The text was translated by Marsilio Firino and immediately it was realised that the symbology of the Christian Faith and the symbology of the late classical myths were saying the same thing. Thats what inspired Renaissance art. Botticelli is full of it, and Michelangelo, and the whole lot of them. This gave a new vitality to the Christian imagery itself. Because they understood its spiritual sense, not its historical reference. Do you see? The reference is not to something that happened which has released us from sin. It didnt release us from sin. What the crucifixion did was give a model so you could release yourself from it…This is the big inspiration of Renaissanc Art.”(Pages 212-213)
We know from Michelangelos letters that he possessed a melancholic disposition and sought though his art to find strength to live a difficult life. He restored lost archaic objects through his art and thereby sought to restore in his appreciators an Ancient idea of “balance of mind”. He, like Shakespeare,was religious: perhaps in the spirit outlined above by Campbell: A spirit in which some of the teachings of the Church could be challenged aesthetically in the name of “artistic licence”. This challenge manifested a freedom of thought valued by the Ancient Greeks.
Adrain Stokes, a Kleinian Art Critic, uses psychoanalysis to interpret the spirit of art-works, especially those from the Renaissance period which he categorised as “QuattroCento Art”. Stokes points to two important aspects of the work of Art: firstly its tendency to “envelop” the appreciator( draw them into its world), and secondly, the tendency of the work to express the independent nature or self sufficiency of the art-object in the Heideggerian spirit of “putting truth to work”. This kind of practical truth belongs of course in the domain of the Aristotelian Productive sciences, which include artefacts and aesthetic objects. Campbell’s expression “transparence to transcendence” is perhaps another way of making the same point.
Michelangelo’s sculpture, “Times of the Day” at the entrance to the Medici tombs feature a melancholic array of figures depicting , day, night, evening and dawn. They have lost their Princes and are in mourning. The mass-effect of the stone, and the suggestion of movement are expressing the weight and difficulty of life (psuché). In this work beauty and sublimity dwell side by side and the effect is that we participate in the difficult life of the Medicis, and in their death. We, participate at a disctance(the aesthetic distance); who knows what the life of a Prince must be like? We moderns have certainly forgotten. Who knows what the life of a God is like? This too we moderns have forgotten. The distance, of course , allows us to judge both Princes and Gods and that fact expresses well the Kantian declaration of the power of Humanism expressed in the Principles “Nothing too much!” an “The Golden Mean”.
Campbell raises the question of Naturalism in relation to the issue of the search for a planetary myth and suggests the possibility of modern film, only to reject this art-form on the following grounds:
“Naturalism is the death of Art. And thats one of the big problems in our American Arts. I think they dont understand the metaphor. Its all naturalism”.
The film “Star Wars” is of course a different genre for Campbell, because, as he says, Lucas the director, understands metaphors, in particlar metaphors related to human psuché via the interaction of man with machine. The machine, according to Campbell, is a metaphor for the totalitarian state and the faceless bureaucrat. This admiration for Star Wars occurs against the background of an admiration for Spenglers work “The Decline of the West”. A society is organic, like psuché, Campbell argues, it is born, matures and ages like all forms of life. The latter aging process is obviously a process of decline. Campbell elaborates upon this theme with the thoughts of Goethe relating to the “Ages of the Spirit”. The first phase is a poetical mythical period followed by a phase he called “naturalistic prose”. Goethe concludes his reflections with the thought that out of such a phase “God himself could not generate another world”. Campbell’s respinse to this point is:
“but I do think we are at the end of a civilisation. And I do think we’re at the beginning of a Global Age.” (Pages 247-248)
We have argued earlier that since Kant we have been living in the Age of the Free Will. Campbell argues that music is the sound that awakens the will:
“The rhythm of the music awakens certain life rhythms, ays of living and experiencing life.”(Page 261)
When music is joyous it lifts the heart, but when it is sad, we, like Buddha, need to participate joyfully in the sorrows of the world.
Views: 121

The inscription on Kant’s gravestone reads: “Two things fill the mind with awe and wonder, the starry heavens above and the moral law within”. Mythology shares Kants cosmological concerns but perhaps not his moral concerns. The cosmos, for Ancient Mythology:
“is normally represented as repeating itself world without end.”
The four fundamental basic elements of water, earth, air and fire will, Myhtology contends, all take turns in the termination of a period of the cosmos/world. According to the Aztecs we are currently waiting for fire to consume the universe. There is nothing moral or tragic in such rounds of ruin and destruction unless of course we imagine the destruction of all forms of life every time a period comes to its end. In this cyclical view of the cosmos the first phase is constituted by the formlessness of chaos which is transfigured into various forms, including the forms of space and various material bodies such as the planets, moons and stars. Life emerges in the next stage of transfiguration which includes animals in both male and female form. One way of characterising this evolution of forms from the state of chaos is to claim that the One is transformed into the many. Various types of myth refer to the forces operating in this transformation of chaos into Being, and Aristotle we know delves deep into the metaphysics of this state of affairs by claiming that “Being has many meanings”. But, Campbell claims:
“Herein lies the basic paradox of myth: the One breaks into the many, destiny “happens” but at the same time is “brought about”. From the perspective of the source, the world is a majestic harmony of forms pouring into being, exploding and dissolving. But what the swiftly passing creatures experience is a terrible cacophony of battle cries and pain. The myths do not deny this agony (the crucifixion); they reveal within, behind and around it essntial peace (the heavenly rose) Pages 246-247)
A prevalent theme recurs, namely, The mother universe as a common reference point in both Oriental and Occidental Myth:
“She is the personification of the primal elements named in the second book of Genesis, where we read that “the spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters”. In the Hindu myth she is the female figure through whom the Self begot all creatures. More abstractly understood, she is the world bounding frame:space, time, and causality. “( Page 255)
Mother Universe must obviously be conceptually ,a virgin and this is symbolised in Christian Religion by the Virgin Mary, mother of God, who is the symbol of this female spiritual creator. Campbell, in a section entitled “The Function of Myth, Cult, and Meditation” claims the following:
“In his life-form the individual is necessarily only a fraction and distortion of the total image of man. He is limited either as male or as female: at any given period of his life he is again limited as child, youth, mature adult, or ancient; furthermore in his life role he is necessarily specialised as craftsman, tradesman, servant, thief, priest, leader, wife, nun or habit: he cannot be all. Hence the totality–the fullness of man–is not in the separate member, but in the bodyof society as a whole: the individual can only be an organ. From his group he has derived his techniques of life, the language in which he thinks, the ideas on which he thrives; through the past of that society descended the genes that built his body.If he presumes to cut himself off, either in deed or in thought or feeling, he only breaks connection with the source of his existence.” (Page 330)
Perusing our modern world Campbell claims:
“There is no hiding place for the gods…; there is no such scoiety any more as the gods once supported. The social unit is not a carrier of religious content, but an economic-political organisation…..And within the progressive societies themselves, every last vestige of the ancient human heritage of ritual, morality and art is in full decay.”(Page 334)
Campbell elaborates upon these points by claiming that the focus of life has shifted from the society to the individual. This shift, he argues, is not in accordance with the oracular proclamation to “know thyself!” if we are to avoid ruin and destruction, but rather involves a rejection of religious belief and myth as subjective falsehoods. What was once transcendental truth, has now become, in the eyes of many moderns, palpable lie or illusion. Furthermore the realm of the sacred has been divested of its meaning in favour of a world view expressed in terms of a totality of facts. Aristotle, we know objected to such a world view by claiming that we do not want just to know what something is, but we also desire to know why it is as it is. Campbell expresses this poetically:
“where light was, there now is darkness” (Page 334)
This in turn helps to define the quest of the hero which is:
“To bring light again to the lost Atlantis of the co-ordinated soul” (Page 334)
The human aporetic problem throughout the ages has been essentially the same: to bring the psuché with its long period of childhood and dependency upon others to a state of maturity in which the individual is independently self-sufficient. This is not a simple task given the conditions of contemporary life, they:
“are what have rendered the ancient formulae ineffective, misleading, and even pernicious.The community today is the planet not the bounded nation, hence the patterns of projected aggression which formerly served to coordinate the in-group can now only break it into factions. The national idea with the flag as totem, is today an aggrandizer of the nursery ego, not the annihilator of an infantile situation. Its parody rituals of the parade-ground, serve the ends of Holdfast, the tyrant dragon, not the God in whom self-interest is annihilated. These words were written in 1949 or before and contain much oracular content.”
One of the Philosophical questions preoccupying the discipline of Philosophy since Kant formulated it, is “What can we hope for?” and it certainly appears that we moderns have no convincing answer to that question unless it is a wish to return to a previous status quo that we appear to some to have outgrown. Kant’s Elightened answer to this question lingers on in the Philosophical waiting room, namely, a Cosmopolitan Kingdom of Ends in which people treat each other maturely as ends-in-themselves in a globalised cosmopolitan world. This vision, it ought to be emphasised lies , according to Kant, one hundred thousand years in the future. It would therefore be premature some 250 years after the proclamation of this vision to definitely determine whether we are progressing toward the end of this hidden plan for psuché, or alternatively, regressing backward to a darker fate. Given the fact that Campbell has in his works appealed to the ideas of Kant it is not entirely clear that he subscribes to the Kantian proclamation of a hidden plan, but he does refer quite often to Freud who called himself a Kantian Psychologist.
Many modern and contemporary Philosophers paint a darker picture of our future, claiming in answer to Kants question that we dare not hope for too much. Hannah Arendt has contributed significantly to this discussion by charting some of the mechanisms that have divided us into warring factions and have also contributed to the emergence of tyranny and totalitarianism which in fact was a fear of the ancient Greeks who saw clearly and distinctly the consequences of striving for both unnecessary and unlawful desires. On her account, evil is banal and merely the result of a failure to think in the way we once were capable of thinking. Her method was both Historical and Philosophical. Freud, also contributed significantly to this discussio in his work “Civilisation and its Discontents”, published in 1929. In his later works we know he condemned Religion on the grounds of its unnecessary desires which assisted in maintaining humanity in a childish state of dependence upn an idea of the divine which may be a chldhood fantasy. Following these authors we have in earlier works designated our modern era as “The Age of Discontentment”, constituted as it is of an array of substitute satisfactions and distractions that have no holistic telos.
Campbell paints a dark picture of our modern times:
“The universal triumph of the secular state, has thrown all religious organisations into such a definitely secondary , and finally ineffectual position, that religious pantomime is hardly more today than a sanctimonious exercise for Sunday Morning, whereas business ethics and patriotism stand for the remainder of the week….And this is not a work that consciousness itself can achieve…The whole thing is being worked out on another level through which is bound to be a very long and frightening process, not only in the depths of every living pscyhe in the modern world but also on those titanic battlefields into which the whole planet has lately been converted.” Page 335)
Campbell also points out that in the course of the secularisation and globalisation processes, the symbol has lost its significance for us moderns. He notes that the causal cosmic laws have, during the course of the above processes, been transformed from an expression of a principle governing particular kinds of phenomena, to a mechanical connection of two events with one another. In the course of this reduction of the symbolic value of the world, e.g. the heavens, animals, plants etc, we are now confronted with the mystery of human psuché which needs to be reconceived in the new emerging framework of mechanical terms. Is the individual hero such a conception?
The individual as a child is essentially narcissistic and resistant to the actualisation processes tempered by the reality principle. This self-actualisation process is part of the maturational cycle which is attempting, in Campbell’s words to convert the “I” into a “thou” in accordance with the mythical proclamation, “Thou art that!” It is this transcendental proclamation that suggests we many are part of the “One.
We have maintained that there is a difficulty in interpreting the term psuche in philosophical discourse which perhaps resulted in not converting the “I” to a thou”, but rather dissolving the “I” into a network of causal processes in which the “I” disappears into a bundle of perceptions, memories, thoughts etc. The Greek mythological figure of Psyche, the goddess, and her relation to eros, who both Socrates and Plato argued, was not a God, is a narrative tale about human Psuché. In this tale, eros is always active and doing something while psyche is preoccupied with just being a woman. In our mother society Campbell argues that the institution of marriage has actually been transformed by the troubadour tradition of the 12th century. Love between two lovers whose eyes meet and whose herts race, becomes, in this tradition a psychological issue rather than , as it was during these times, a family issue, where the family would decide whom one marries. Thus began one of the major transformations of the concept of human psuché: a transformation which moved away from the Aristotelian essence specifying characterisation, namely, “man is a social animal” and moved toward a focus on the individual egocentric “I” who becomes more important than the family and village, even to the extent of ignoring the marital status of those opposite sex partners one finds attractive.
The French concept of Amor” characterises this condition very well. Rousseau, working in the Romantic tradition, invents an ideal pupil to raise and educate in this Romantic tradition. Emile, the pupil is not permitted to read the Bible but is encouraged to read works such as Robinson Crusoe–a man marooned on a desert island and forced to provide himself with the necessities of life for survival in a state of nature. Rousseau could be seen to be a figure resembling that of Diogenes, sensing as he does in the dark recesses of European society a discontentment which he both describes and explains brilliantly.
Rousseau was both a Counter- Enlightenment figure who also claimed :
“Man is born free but everwhere in chains.”
in the spirit of both romanticism and naturalism. Yet we ought also to recall that Rousseau dismissed many Aristotelian ideas and given the fact that Kant was elaborating upon hylomorphic ideas, he would have dismissed many of Kant’s rationalistic premises. Kant’s work “The Conjectural Beginnings of Human History” suggested in hylomorphic spirit that it is the business of Reason to Regulate the Passions especially when they tend to excess and violate the Aristotelian principle of the Golden Mean. For Kant, the concept of the “noble savage”was a naive populistic idea glorifying the pre-civilisational condition of a state of nature which restricted the repertoire of needs and wants that civilised beings desire.
For Rousseau,the inequalities produced in the course of mans social strivings for wealth and power, results in a disposition Rousseau names “amour-propre”, a form of social relation connected to the dispositions of pride, vanity, conceit, and egocentrism. This so called “civilised” form of amour, Rousseau contrasts with the natural form of self-love we encounter in Robinson Crusoe whose primary need is to make himself as comfortable as possible in a state of nature. This kind of solipsistic naturalism, where the individual is splendidly isolated, was to reverberate down the centuries all the way to the early work of Wittgenstein (Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus) Wittgenstein, in his later work,(Philosophical Investigations) recognised in his early work a commitment to what he himself called logical solipsism which could not be defended if one was to focus on the social activities of man embedded in social forms of life playing many “language-games” as part of a demonstration of a master of language.”
Views: 154

Campbell, in his work “Occidental Mythology”(London, Souvenir Press 2001) noted that the Age of Heros and Gods extended from 1520-500 BC, and this Era was succeeded by the Age of the Great Classics which, in turn, extended from 539 BC to 500 AD. Campbell also notes in this work the fundamental differences that exist in Oriental Mythology when compared to Occidental Mythology. In the former, Campbell notes that:
“Prayers, chants, images, temples, gods, sages, divinities and cosmologies, are but ferries to a shore of experience beyond the categories of thought, to be abandoned on arrival.” (Page 3)
Man and God, in this system, are not opposites but transcendentally identical entities. Occidental Mythology maintains that man has not the power for such an experience but can only experience the” divine within himself”. There is, Campbell argues, a movement between The Book of Job in which man abandons his human judgement in favour of that of God, and the competing mythology of the Greeks, who dare to stand independent and free with their knowledge of themselves and their world, and who also dare to judge the characters of their Gods: thus initiating a humanistic tradition that was continued in European Mythology(Greek, Roman, Celtic and German.) In these systems, Logos as the Word of God, and the rationality of human psuché, are contrasted, and give rise to very different views of God and Man, and their relation. In his account of the Cultural development of Man Campbell notes that in ca 7500BC in the Near East Region of Asia Minor, Syria, Northern Iraq and Iran:
“The arts of agriculture and stockbreeding were developed…..men now became substantial tillers of the earth. Self sustaining villages appeared and their number steadily increasing, spread in a broad band eastward and westward, arriving simultaneously at both oceans about 2500 BC. Meanwhile, in the developed Zone of origin, the nuclear Near East, a second epochal mutation occurred ca 3500BC when in the river land of Mesopotamia the fundamental arts of all high civilisation were invented:writing, mathematics, monumental architecture, systematic scentific observation (of the heavens), temple worship and the kingly art of government.” (Pages 6-7)
Aristotle’s political view of man, the rational social animal, is in accord with the above quote. His idea of the self-sufficiency of the village provided a social framework for the family to meet more complex needs which would then, in turn, develop into the need for the village to unite with other villages and form a polis which demanded that the art of government become more organised and more complex, and perhaps demanded the invention of the other arts and sciences as well. Thousands of years of the practice of these arts and sciences take us up to the date of 1200BC, the date Julian Jaynes, the Princeton Psychologist, claims the power of Consciousness emerged as a broad social phenomenon.
Language, up until this point in time was, Jaynes maintains, bilaterally located in the brain. Jaynes further controversially maintained that the voices of gods and Kings were transmitted between the hemispheres in te form of commands: these gods and Kings themselves may, or may not, have possessed the power of consciousness, which according to the Delphic oracle demanded of man that he know himself if ruin and destruction was to be avoided. Jaynes’ hypothesis builds upon brain research and the discovery that the right hemisphere also possesses a capacity to recognise language.
Campbell notes that around the date 1250BC in the Occident:
“The old cosmologies and mythologies of the goddess other were radically transformed, reinterpreted, and in large measure even suppressed by those suddenly intrusive patriarchial warrior tribesmen whose traditions have come down to us dually in the Old and New Testaments and the myths of Greece.” (Page 7)
We have pointed out previously, in the context of the above debate, that Greek mythology had possessed in turns the female figures/furies of the Erinyes, the Oracles, who tended to be female, and the Goddesses of the Zeus Pantheon. This suggests a significant appreciation of the role of the female in what Ricoeur called “the realm of the sacred”.
Campbell, in his work “The Hero with a thousand faces” develops the theme of the goddess via the thought of Melanie Klein contained in her work, “The Psychoanalysis of Children” Klein, for example, notes that if the infant is deprived, for some reason of the breast, its fury can become quite alarming for bystanders:
“These appear as reactions to, and spontaneous defences against the body-destructive fantasies that assail the child when it is deprived of the mothers breast.The infant reacts with a temper tantrum and the fantasy that goes with the temper tantrum is to tear everything out of the mothers body……The child then fears retaliation for these impulses, i.e. that everything will be scooped out of its inside. Anxieties for the integrity of its body, fantasies of restitution, a silent, deep requirement for indestructibility and protection against the “bad” forces from within and without, begin to direct the shaping of the psyche, and these remain as determining factors in the later neurotic, and even normal life activities, spiritual efforts, religious beliefs, and ritual practices of the adult.” (Page 149)
Campbell points to the medicine men of primitive tribes as emerging from such body-destructive fantasies. The medicine man attempts to restore the integrity of the body for the imagination. Childhood fantasies do not manifest themeselves merely in the rituals of primitive peoples, but also in their myths. These manifestations occur in many forms including that of immortality and the separation of the soul and the body.
The Hero, Campbell argues, seeks intercourse with the gods and goddesses and the Imperishable Being that transcends them both. In the Eastern Mythologies this experience of immortality is not tied to the separation of the soul and the body but rsther to an experience of the immortal as a presence in the moment.
Having found what he was searching for, the hero is then destined to return to the kingdom of humanity with his message which even Buddha doubted could be communicated. What is the message which is so difficult to understand? Campbell suggests the following:
“The realm of the gods is a forgotten dimension of the world we know. And the explanation of that dimension, either willingly or unwillngly, is the whole sense of the deed of the hero. The values and distinctions that in normal life seem important disappear with the terrifying assimilation of the self into what formerly was only otherness.” (Page 188)
Both Plato and Buddha ask whether the hero, having experienced the world of forms, can return to humanity, without either danger to themselves, or the frustration of trying to communicate a message that transcends common sense. Hinduism speaks, for example, of the battlefield:
“The battlefield is symbolic of the field of life where every creature lives on the death of another…The goal of the myth is to dispel the need for such life ignorance by effecting a reconciliation of the individual consciousness with the universal will. And this is effected through a realisation of the true relationship of the passing phenomena of time to the imperishable life that lives and dies in all. ..Man in the world of action loses his centering in the principle of eternity if he is anxious about the outcome of his deeds but resting them and their fruits on the knees of the living God he is released by them, as by a sacrifice, from the bondages of the sea of death.”(Pages 205-206)
This reminds us of the the message fro the Bhagavad Gita:
“I am death the destroyer of worlds”
uttered in the name of the life principle (eros) which the Ancient Greeks struggled so valiantly to comprehend. The search of Philosophy for the Eternal Forms or Metaphysics (Aristotle’s first principles) is neither mythological, biographical, historical or scientific. Campbell laments:
“Whenever the poetry of myth is interpreted as biography, history or science, it is killed. The living imges become only remote facts of a distant time or sky. Furthermore, it is never difficult to demonstrate that as science or history, mythology is absurd. When a civilisation begins to reinterpret its mythology in this way, the life goes out of it, temples become museums, and the links between the two perspectives is dissolved. Such a blight has certainly descended on the Bible and on a great part of the Christian Cult. To bring the images back to life, one has to seek, not interesting applications to modern affairs, but illuminating hints from the inspired past. When these are found, vast areas of half-dead iconography disclose again their permanently human meaning.”(Page 213)
Both Mythology and Philosophy, in their different ways concern themselves with the wisdom, forms and principles from the past. Each religion in its different way also contains the transcendental experiences typical of the “realm of the sacred”. Campbell, like TS Eliot is a Catholic. He describes the Christian experience of “Holy Saturday”(The day between the death and resurrection of Christ):
“… the priest puts on a purple cope and, preceded by the processional cross, the candelabra and the lighted blessed candle, goes to the baptismal font with his ministers and the clergy, while the following tract is sung: “As the hart panteth after the fountains of water, so my soul panteth after thee, O God! When shall I come and appear before the face of God? My tears have been my bread day and night, whie they say to me daily:Where is thy God?”(Page 214)
This melancholic lament recalls the message Jaynes refers to in his explorations of the existence of God during the period of the dawn of Consciousness: the message, namely, of a Deus Absconditis which has been crassly and popularly translated by Nietzsche into the crass message of God being dead. It is, Jaynes argues, we who bear the responsibility for both the historically experienced presence of God and his/her absence. The task of mythology, more than Philosophy, is to restore this archaic experience of transcendence in our lives. Modern Catholicism, of course, is imbued with the spirit of Romanticism as the above experience of Holy Saturday clearly manifests. The Priest-King or Grail-King is the Romantic hero that symbolises the tragedy of the life of Christ. In this Holy Saturday ceremony, the familiar waters of transformation is blessed in the hope that the Holy Ghost will “cleanse” the water of all traces of “Satan”. Water is the sacred substance of baptism which John used to baptise Jesus and provide us all with the experience of being born again, washing away original sin in the human form of psuché.
In a section entitled “From Psychology to Metaphysics”, Campbell notes that the symbols of mythology resemble the elements of dreams and he also notes that the psuchoanalysts( Freud, Jung, Stekel, Rank, Abraham, Klein, Roheim, etc) have provided us “with a store of common principles” (Page 219) by which to interpret both types of phenomena. Of course, the scientific view of the world as “the totality of facts”, stands in the way of such interpretations, construing them as “false”, because subjective, as if the individual element of our experience needed to be cancelled if the scientific form of “The Truth” was to prevail.
There is no doubt, however, that the Transcendental form of reasoning in the analogies found in Kant’s Prolegomena (used by Campbell in his work “The Outer Reaches of Inner Space”) are in a sense “relational truths”. Campbell argues that transcendental analogy provides us with some access to the “realm of the sacred”, or what Campbell refers to as “the morphogenetic field”.
Campbell sees a close resemblance between the phenomena of dreams and the experiences related in myths. One crucial difference is that in the case of myths the elements are consciously chosen for the purposes of communicating what is transcendent. In that respect myths are a more structured form of experience designed to manifest the “vital energies of the whole human psyche”. These elements:
“Link the unconscious to the fields of practical action, not irrationally, in the manner of a neurotic projection, but in such a fashion as to permit a mature and sobering, practical comprhension of the fact-world, to play back, as a stern control, into the realms of infantile wish and fear.” (Page 220)
Myth, that is, are:
“controlled and intended statements of certain spiritual principles which have remained constant throughout the course of human history as the form and nervous structure of the human physique itself.” (Page 221)
One of the keys to understanding the divine power within is given to us by Aristotle’s power of “noos”, the divine part of the human form of psuche which can be accessed by the so-called great-souled-beings (Phronimos), who are able to use pracitcal rationality to both know themselves and avoid the ruin and destruction predicted by the Oracles. Campbell finds this idea well expressed in the Gnostic Gospel of Thomas:
“The Kingdom of God is within You”
Views: 114

Creation myths often speak of a first created Being that is androgynous , e.g. Adam, Eros, Hermophrodite, Awanawilona,(Pueblo divinity), Tiresias, Tai, Yuan, etc. The genders of male and female are construed as opposites and this in turn demands a dialectical form of description/argumentation because, when apprehended as opposites, it appears as if one opposition term is the negation of the other.
Campbell contrasts the Buddhist position related to Peace in the World with the World Redeemer of Christianity, namely Jesus, and he also notes that Christianity is associated with a partisanship in which the laws of De Civitate Dei appear to apply to a chosen group of people, and this has the military consequence that holy wars are permitted against all the non-chosen “barbarians”. He supports his argumentation by noting that Christian Nation States have a history of “colonial barbarity” and “internecine strife”(Page 134). Marching under the flag of the cross, Campbell argues, is not, however in accordance with the democratic symbol of the cross which is perhaps connected to the wider theme that “All Men are Brothers”. Campbell, proclaims in the context of thisdiscussion that it is to the Eastern Religions we must turn for an account of the experience of the “Transcendental Everlasting”:
“Those who know, not only that the Everlasting lives within them but that they, and all things, really are the Everlastng, dwell in the groves of the wish fulfilling trees, drink the brew of immortality, and listen everywhere to the unheard music of eternal concord. These are the immortals. The Taoist landscape paintngs of China and Japan depict supremely the heavenliness of this terrestrial state.” (Page 142)
Given that the transcendental quality of Being is in a sense beyond thought and beyond speech, it is difficult to contest the picture we have been provided with above. The Philosopher Spinoza is usually referred to as the Philosopher of the Infinite. Much of his work has a hylomorphic character, but he refers not to the infinity of forms but rather to the infinity of modes of God or Substance. God or Substance, for Spinoza, is only accessible by human forms of psuché via the modes of thought and extension, two modes of a possible infinite number of modes. The mode of thought, for Spinoza, is primarily composed of the idea of the object of the body which is also part of the mode of extension, which in its turn is part of the idea of psuché. On this theme, Spinoza claims in his work “Spinozas ethics” in a section entitled “Nature and Origin of the Mind”:
“The idea which constitutes the formal being of the human mind is the idea of the body, which is composed of many individuals, each composed of many parts……Therefore the idea of the human body is composed of the many ideas of the component parts.”(Translated Boyle, A.,London, Aldine Press, 1910. Page 53)
It is clear that the ideas of the mind are not enclosed within their own domain but rather reach out to the external world, and in this process perception is an important power of the body/mind:
“All modes in which any body is affected follow from the nature of the body affected, and at the same time from the nature of the affecting body. Wherefore the idea of them must involve necessarily the nature of each body. Therefore the idea of each mode in which the human body is affected by an external body involves the nature of the human body and that of the external body….Hence it follows in the first place that the human mind can perceive the nature of many bodies at the same time as the nature of its own body. It follows in the second place that the ideas which we have of external bodies indicate rather the disposition of our body than the nature of its own body.” (Page 53)
Kant would subscribe to much of the content in the above quotes and this may not be surprising given that both Philosophers espouse forms of rationalism similar to that of Aristotle. Spinoza believes his Work “Ethics” possesses a mathematical/geometrical structure of arguments which constitute “proofs”. This, of course, is in contrast to the methodologies of both Aristotle and Kant who both wrote in normal academic prose. Spinoza, in this work, also provides us with accounts of the powers of imagination and memory, which both Aristotle and Kant would largely ascribe to. Imagination, Spinoza argues:
“Again, to retain the usual phraseology, the modification of the human body, the ideas of which represent to us external bodies, as if they were present, we shall call the images of things, although they do not recall the figures of things, and when the mind regards bodies in this manner we say it imagines them…And here, so that I may begin to point out where lies error, I would have you note that the imaginations of the mind, regarded in themselves, contain no error, or that the mind does not err from that which it imagines, but only insofar as it is considered as wanting the idea, which cuts off the existence of those things which it imagines, as present to itself. For, if the mind while it imagined things not existing as present to itself, knew at the same time that these things did not in truth exist, it would attribute this power of imagination to an advantage of its nature, not a defect, more especally if this faculty of imagining depends on its own nature alone, that is,if the mind’s faculty of imagining be free.” (Page 55)
Spinoza characterises memory in the following terms:
“If the human body has once been affected at the same time by two or more bodies, when the mind remembers any one of them it will straightway remember the others…..For it is nothing else than a certain concatenation of ideas invoking the nature of things which are outside the human body, and this takes place in the mind according to the order and concatenation of the modifications of the human body.” Pages 55-56)
Spinoza then adds the following remark:
“the mind and the body, are one and the same individual.”
This is an important claim given the historical Cartesian penchant for opposing thought and extension as two different substances, a position modern science largely accepted and adopted in relation to giving an account of psuché. Cartesian dialectical reflection is also involved in the conflict of religions where the central idea appears to be that your God is not my God, not the real God. Indeed, for Spinozas understanding real oppositions such as male and female require adequate ideas for both forms of human psuché which we perceive clearly and distnctly in relation to their logos. Spinoza elaborates upon this theme in the following manner:
“I say expressly that the mind has no adequate, but only confused knowledge of itself, of its body, and of external bodies, when it perceives a thing in the common order of nature, that is, whenever it is determied externally, that is, by fortuitous circumstances, to contemplate this or that, and not when it is determined internally, that is by the fact that it regards many things at once, to understand their agreements, differences, and oppositions , one to another. For whenever it is disposed in this or any other way from within , then it regards things clearly and distinctly.” (Page 62)
The Philosophical conception of science embraced by both Aristotle and Kant includes that of theory which “regrds many things at once” in relation to their “agreements, differences and oppositions”. Philosophical science, in other words, provides us with adequate ideas of the genre and species of psuché, to take one example from one domain of science.
Insofar as psuché is concerned, Spinoza argues that that our idea of this is “very inadequate”:
“We have only a very inadequate kowledge of the duration of our body.The duration of our body does not depend on its essence, nor even on the absolute nature of God; but it is determined for existng and acting in a certain determined ratio by other causes, and these by others, and so on to infinity. Therefore the duration of our body depends on the common order of nature, and the disposition of things. But there is in God an adeqaute knowledge of the reason why things are disposed in any particular way, insofar as he has ideas of all things and not insofar as he has only knowledge of the human body. Wherefore the knowledge of the duration of our body is very inadequate in God insofar as he is considered as constituting only the nature of the human mind, that is, this knowledge is very inadequate in our mind.” (Pages 62-63)
This, of course, is an issue touched upon by the Kantian notion of noumenal reality which includes not only the inadequate idea we have of the external world but also the inadequate idea we have of our bodies as well. Kant, of course, beieves that we can have an adequate idea of the freedom of our mental powers to influence our wills and our actions. Spinoza, disagrees claiming that:
“men are mistaken in thinking themselves free.”(Page 64)
Spinoza believes this proposition, on the grounds that the primary idea of the mind is the inadequate idea of the body which is subject to a large number of causes stretching back to infinity. Spinoza goes on to claim that those that say that:
“human actions depend on the will” (Page 64)
do not understand exactly what they are saying. The question to raise in the context of this discussion is: given the fact that God constitutes our mind and our minds therefore possess a divine element or divine ideas, does this mean that freedom, if it exists, is god-given or not? Kant, we know, argues that freedom is causa sui—cause of itself– and this may imply that this is the divine element of ur constitution and the reason why we needed to be commanded in the Garden of Eden by God not to eat from the tree of the kowledge of good and evil and perhaps it is also why we need to be commanded to love our neighbours and God above all. If, however, this is the case, then our lack of knowledge of the causes that produced a constitution possessing the ideas of God and freedom is irrelevant
Some religions such as Buddhism claim that our life is a journey with a beginning and end on a noble pathway. Buddhism has been construed as an Enlightened religion because of its view of the importance of knowledge of the external world and the mind. The external physical world is conceived of in terms of what is described as the “sermon of the inanimate” which the Philosopher Thales expressed in his proclamation that “all things are full of Gods”. Campbell claimes to see this spirit in the Taoist Tea ceremonies. He also refers in this context to the myths of the Apaches and some African mythologies which proclaim that the rocks, fire, and water, are all alive like the plants. This may be a category mistake insofar as thought is concerned for both hylomorphic and critical Philosophy.
The issue of gods and goddesses, the divine opposites, is an important issue for Campbell who claims in this context that:
“For in the language of the divine pictures, the world of time is the great mother-womb. The life therein, begotten by the father, is compounded of her darkness and his light. We are conceived in her and dwell removed from the father, but when we pass from the womb of time at death (which is our birth to eternity) we are given into his hands. The wise realise, even within this womb, that they have come from and are returning to the father:while the very wise know that she and he are in substance one.”(Page 144)
Campbell continues:
“The union of the two is productive of the world, in which all things are at once temporal and eternal, created in the image of this self-knowing, male, female, God.”(Page 145)
We are created in the image of God and this theme of the opposites occupies Campbells attention at the level of the “opposites” of the male thunderbolt symbol and the female symbol of the bell which provides us with the melancholic sound of eternity. The bell summons us to take the noble path to the end, with the understanding that upon reaching the end we know it to be the beginning: opposites become one, including those most puzzling opposites of good and evil. It is at this point thatCampbell cites from the Upanishads whose claim is that when the hero takes the noble path to Brahman all opposites unite, including good and evil into one God, one Substance.
Views: 206

Campbell, in his interview entitled “The Road of Trials” (Pages 52-53) suggests that the things that cannot be talked about are easily misunderstood because they transcend the dialectical orientation of everyday language in which opposites are generated by the negation function of such language which is oriented to everyday circumstances. In such everyday circumstances it is the selfish “I” that is speaking about worldly experiences.
Campbell acknowledges that Psychology has an important role to play in the understanding of man, the rational anaimal capable of discourse, and, of course, his myths. In the context of this discussion Campbell articulate what he sees to be the fundamental difference between Jungain and Freudian Psychology. He obviously has a preference for Jungian archetypal patterns and its home in the collective unconscious which he claims is in contrast to the Freudian notion of a personal unconscious. Freud, in fact, speaks of both forms of the unconscious especially in the later phases of his work where he refers to the battle of the Giants, namely Eros and Thanatos fighting for the fate of our civlisation. Campbell claims that Jung aspouses a more biological universal form of the unconscious that is a function of the effect of our organs on our psychic activity, and this is a hylomorphic view of how the psychic representatives of the unconscious are formed, which Freud undoubtedly in some sense embraced. Freud, of course, also spoke of the personal impact of the traumas of childhood upon the psychological well being of the individual.
Eros and Thanatos are also represented in the artistic genres of Tragedy and Comedy which is a title of a chapter in Campbell’s “The Hero with a thousand faces”. Campbell refers to “amor fati” (the love of fate) which certainly recalls the Delphic proclamation: “Everything created by humans is destined for ruin and destruction”. This proclamation haunted Ancient Greek consciousness, especially in relation to its preoccupation with the powers of the mind and the task of harmonising the powers and their relation with the external world, which, we ought to recall was a central concern of Freudian Psychoanalysis. For Freud, the driving force of unconscious instincts could be both positive (eros) and negative (thanatos), and this together with the aganecy of the ego which was constituted by a precipitate of lost objects helped to create the impression Kant had of everyday life which he described in terms of being “Melancholically haphazard”.
Modernism which according to Arendt, stretches back to Descartes and Hobbes, stretches forward to what Arendt called “This terrible century” (20th century). During this centiry we saw the pendulum of values swing between good and evil, right and wrong, lawfulness and unlawfulness, and we saw moreover, how there was an inversion of these opposites where tyants for example took the right for the wrong and evil for what was good. Many historical events were produced by Arendt in evidence for her judgements on the origins of totalitarianism, but other Philosophers, e.g. Paul Ricoeur, also pointed to the disappearance of the discipline of rhetoric during this period. The event of the divorce between Psychology as a science and Philosophy in in 1870, also testified to the collapse of many traditional political and cultural structures and practices. Stanley Cavell, for example, points to the marginalisation of many aesthetic values during the beginning of the century when so-called modern art began challenging many historical beliefs and practices. Cavell speciifically also drew attention to the refusal to consider the history of the belief or practice of the activity one was engaging in or questioning. Heidegger too, entered the arena of the deabte over the presence of confusion over the translation of key Ancient Greek terms into Latin, claiming that the Latin translations of, for example, aletheia and phusis gave rise to a number of confusions. Wittgenstein, in the period under consideration, pointed to the prevalence of conceptual confusion in the discipline of Psycholgy. P M S Hacker a Wittgensteinian scholar, also pointed out a number of conceptual confusions in the field of neuroscience. Many of these problems can be traced back to a confusion over what can and what cannot be said about the Ancient Greek concept of psuché, the human form of life.
Modern Art of the early 20th century was enveloped by a vortex of controversy, with musical compositions containing no sound, in the name of music, weightless sculptures, in the name of sculpture , blank canvasses, in the name of painting. Wittgenstein claimed that in the classical music of Brahms he could hear the sound of engines. Our contention is that many of the above confusions arise not from local factual misunderstandings but from a fundamental misunderstanding of the principles and categories of thought that are appropriate to use in relation to the concept of psuché, rather than as Heidegger claimed a “forgetfulness of Being”, which, of course, is a more abstract and general characterisation of the problems under consideration. If one accepts this line of reasoning, then one see all the above problems, including the origins of totalitarianism, under the aspect of a systematic misunderstanding of a category of Being. Heidegger however, in his investigations of the human form of Being-in-the-world, highlights the confusions relating to death in everyday dscourse which he argues fails to confront the phenomenon of death meaningfully.
T S Eliot, one of Campbells favourite writers, postulates that our modern world has become a wasteland, which is represented in the mythical figure of the wounded, impotent, Grail King. All of the above indicates the nature of the value of the objects the Ego has been forced to abandon and mourn in a mood edging toward melancholia. What transpires, as a consequence, is a consciousness preoccupied with the events of the external world which evoke the power of the imagination more than the powers of understanding and reason: a state of mind that marginalises the realm of the sacred (Ricoeur) and the Metaphysics of Nature and Morals. What is also implied by the marginalisations of historically important domains of thought, is the following: when the attention of consciousness is constantly trained upon stimulating objects, the emotional and passionate states generated require a return to a state of homeostasis, which is this state edging toward melancholia. This is a passive state which Arendt captures in her characterisation of the masses “for whom nothing is possible anymore”.
God may either be dead, or merely deus absconditis, for the modern wastelanders, who see “fear in a handful of dust”. T S Eliot we know, in his later life, sought redemption in the Christian Faith. His poem “Four Quartets” is about Time and a Spiritual Journey that circles back upon itself, tofind itself back at the beginning of the journey, but wiser for the experience, possessing more knowledge of the world and oneself. Where we are currently on this journey was earlier characterised in terms of a “wasteland”, but this situation in the “Four Quartets” is nevertheless conceived of in more positive terms of a life which can understand how formless our lives in general has become.
The tragic pair of Pity and Fear are, of course, present in different ways in Eliot’s poetry but he does not embrace the conceptual framework of Ancient Greek thought, preferring the framework of Catholicism and its fixation upon the Grail King, sacraments, and visions of heaven and hell which Campbell believes is merely a local ethnographic perspectival vision of the realm of the sacred and the divine that he believes takes us no closer to the goal of providing humanity with a universally valid planetary myth or religion. Knowledge and Rationality does not play the central role it plays in Ancient Greek Philosophy which rests upon the ideas of areté, arché, diké logos, aletheia, psuché, phusis, phronesis and eudaimonia.
The Ancient Greek conception of techné presupposed epistemé, areté, logos, psuché and aletheia, but this conceptual framework has been abandoned by the modern world largely because our modern science has limited itself to the goal of the quantification of nature via the use of the method of observation in a context of exploration: a use which rejects many rational principles, e.g. the principle of sufficient reason. The spirit of Newtonain and Kantian science was one which embraced a set of first, rational principles that the scientist approached nature with, in the spirit of a judge who puts conceptual questions to nature and expects answers in accordance with those first principles. This modern spirit of science is so difficult to characterise because of its limited focus, and its increasing complexity. What can be said, is that it is certainly embedded in a technological network of Heideggerian instrumentalities that always seem to refer beyond themselves in the sense of being “for-the-sake-of”. For the Acient Greeks, techné was situated in the domain of the productive sciences which included sculpture, builders, carpentry and weaponry, but did not include medicine, mathematics and rhetoric, all of which had intimate relations to the rational basic ides of aletheia, eåistemé and logos.
Psychoanalysis would, then, on the above account, be a skill, a technique, and an intellectual discipline. Epistemé for the Ancient Greeks was certainly a higher intellectual power and a superior form of knowledge obeying intellectual rational principles. Knowledge does not belong in the same category of instrumentalities which are not ends-in-themselves but rather means to ends or, as Heidegger expressed the matter, that “for- the. sake-of”. Instrumentalities, in other words, are cause-effect relations and do not have a telos connected to the more categorical forms of arché that we find situated in the context of explanation/justification.
The Arts of Tragedy and Comedy, as practiced by Shakespeare, occurred over a century later than the “times of the troubadour”, and several centuries later than the age of chivalry, which initated for Campbell, the romantic form of individualism he believes is central to our Western identities. Shakespeare skillfully combined these themes with the themes of Ancient Greek tragedy and Philosophy, that were being reawakened during the Renaissance. God, during the time of Shakespeare, was still an important presence, but the star of Religion was waning in importance in the light of the Protestant Revolution. Many Renaissance artists, such as Michelangelo, remained intensely religious, but were becoming more courageous in their challenges to the authority of the Church insofar as the limitations imposed by the church upon what they may or may not represent was concerned.
Science, too, with the invention of the telescope, was making space for itself in our everyday life, which now knew we were actively exploring the heavens and the movement of the stars and planets. The space of infinity and the time of eternity, were now transforming the activity of observing the heavens with a discipline which would become the discipline of astronomy. We were challenging the magnitude of the physical universe and thereby becoming so much more than a handful of dust reminding us of the lost object of a life that was no more because its powers had been extinguished. The transcendental attitude was being restored, but at the same time narrative accounts relating to the the place of the heavens, where wandering souls were domiciled, became less plausible. The image of ghosts and one soul leaving a body and entering another, was, of course, an image of the imagination which was not connected to reality in the way in which the memory or consciousness was.
Heraclitus claimed that the logos of change was to understand that two phenomena such as the road leading up the hill and the road leading down the hill were to be thought of as in soem sense the same. Aristotle saw the principles of change to be manifested in kinds of change, principles, media and causes: e complex network of considerations which was in accordance with logos, epistemé, and aletheia, which three different domains of science could investigate. These domains of science of course concerned themselves with psuché in different ways given that they related to knowledge and skills of different kinds, and given that explanations and justifications. Such explanations and justifications occurred in relation to the many principles regulating all the changes in the natural world as well as the changes in the the world of psuché.
Campbell points out that the narratives of myth are about the changes the hero undergoes in the course of his/her heroic quest, and many of the events are dreamlike, because, presumably, the changes we are witnessing are being processed by the imagination and the emotions that are being evoked by outer changes. Dreams require interpretation because they too are products of inner psychic change in the medium of images which resemble in many respects the images of film that Stanley Cavell discussed in his work “The World Viewed:Reflections on the Ontology of Film”. The imges of film, in contrast to our dream images, are automated, and the objects photographed “participate” in “the photographic presence of themselves on film”: making them, in fact, more like memories than the images of dreams (which are inserted in a wish-fulfillment complex). The dreamlike quality of film is difficult to analyse, but they too, in some sense, relate to the imagination and passions of the creator of the plot of the film. This, added to the fact that there is a form of “technical intelligence”, involved in the automation process which relates to instrumental forms of reasoning connected to the instrumental notion of “for-the-sake-of”. The camera, moving over a landscape, from object to object is an imitation of sensory experience: an automated form of sensory experience which is very different to that form that occurs in relation to a human body (the human body, that is, possesses a sensori-motor unity based on a constellation of organs and limbs typical of the human form of life(psuché)). Cavell is suggesting here that the moving automated images and mechanically induced movement of the film camera, provide us with a sense of a Being-in-the-world which is not human. The lack of real depth in the movement of the photographic images also suggest the lack of the presence of many categories associated with the understanding of human movement, because as Brian O Shaughnessy suggests:
“concepts play a causal role in the genesis of visual depth experience.” (The Will: A Dual Aspect Theory”. Page 171)
Films imitate the depth of three dimensional space in two dimensional images, and everything viewed “participates” in the real forms of the world and this might partly explain the dreamlike quality of the film experience. There is no suggestion that Campbell believes that our modern art-form of film-making could be the basis for the Planetary mythology he is seeking.
We have questioned the metaphysical status Campbell attaches to the hero, equating as he does the hero with a God in his work “The Hero with a thousand faces”. Overcoming overwhleming forces and manifesting supernatural powers against terrifying monsters are certainly not as realistic as the Socratic responses to the overwhelming forces he was confronted with. Socrates of course was not a mythological figure and would have objected to be called a God in the way Buddha was. The Buddha narrative speaks of an unnantural birth and a figure who sits under a Bodi tree “fighting a dark army” led by Kama-Mara. There was not, for Socrates, as there was for Buddha, a King of the Serpents protecting him from various supernatural dangers.
Campbell also refers to Prometheus and his world-transcending deed of stealing fire from the Gods to give to humanity. There is here an allusion to the pre-history of humanity, and the importance of the role of fire in the early phases of the primitive hunting/gathering groups living in caves. The narrative surrounding Prometheus, however, was not a clinical historical account but rather a narrative driven by the passionate desires: a narrative that desired to metaphorically communicate the sacred meaning of certain events in man’s history. Campbell claims that Jungian archetypes were involved in the construction of the Pometheus narrative, in particular the archetype of the Hero:
“Whether the hero be ridiculous or sublime, Greek or barbarian, Gentile or Jew, his journey varies little in essential plan. Popular tales represent the heroic action as physical: the higher religions show the deed to be moral: neverthless there will be found astonishingly little variation in the morphology of the adventure, the character roles involved, the victories gained. If one or another of the basic elements of the archetypal pattern is omitted from a given fairy tale, legend, ritual, or myth, it is bound to be somehow or other implied–and the omission itself can speak volumes for the history and pathology of the example.” Page 30 “The Hero with the thousand faces “
Philosophical mythology would of course not be so concerned with physical world-historical deeds such as those attributed to Achilles , but more concerned with the moral deeds of world-philosophical characters such as Socrates, e.g. his activities in the agora and his relation to death as a consequence of his death sentence by the Athenian courts.
Views: 334

Philip Cousineau in his Introduction to Campbell’s “The Hero’s Journey” claims that Campbell’s search was for the Logos of the phenomena he investigated. The concern, that is, was what these phenomena had in common rather than what differentiated them from each other. The method used was described as comparative historical elucidation and it can be contrasted with the method of Wittgenstein, which sought essentially to differentiate between different phenomena. Cousineau reminds us of the proclamation we encounter in the Vedas, namely:
“Truth is one, the sages speak of it by many names”
In this regard reference is often made to the collective archetypes of Jung, which are used to justify the denotation of many sacred narratives Campbell calls these sacred narratives or myths the “Masks of god” which partly constitute the “morphogenetic field” which we presume is identified with “The Truth” mentioned in relation to the Vedas above. The role of the hero is, we have agued in previous reviews of Campbell’s work, an ambiguous reference, which appears to exclude the quiet contemplative rational transformation Philosophers like Socrates, Plato and Aristotle appear to have undergone in their essentially intellectual journeys. These are the “modern” “pathfinders” in the modern morphogenetic field. We do find Socrates engaged in inner communication with his daemon in life-crisis situations, but Psychoanalysis would have no difficulty in explaining this communication as one between the ego and the superego, in a situation where a choice of life-defining alternative actions are being considered. The life defining experiences of saints, prophets and shamans are of course a much more dramatic affair.
Cousineau claimed that Campbell’s method involved the use of the hermeneutical method. Paul Ricoeur, the Philosopher, articulates well the concern of hermeneutics for “symbols”, claiming that symbols possess the semantic property of “double meaning”. Expressions with a so-called manifest meaning provoke thought to move to another deeper meaning in what Ricoeur calls the “realm of the sacred”, which we mortals seem able to comprehend only through a glass darkly. Kant speaks in his Third Critique of Judgment of a statue of Isis and an inscription that says “no mortal has ever lifted my veil”.
Aristotle refers to this realm in terms of the realm of Being and he further claims that “Being has many meanings” . This concerns not merely our relation to God, but also our relation to life (psuché), death and the mysteries of the external world. Campbell uses the word “metaphor” in its Ancient Greek meaning of “carrying beyond”: a meaning that transcends the more modern interpretation in terms of a shift from one semantic region to another. Reference is also made to the archetypes of the soul in the spirit of aletheia (unconcealment or revelation). We encounter this spirit in the Gnostic Gospel of Thomas which articulates a framework for the “many meanings of Being”, by claiming that the Kingdom of God is both within us and out there in the world, here and now. Eastern Religion also articulates this transcendental feature of our experience in terms of “Thou art that!”.
Ambiguous references to the archetype of the hero and his journey do not, as we have claimed earlier, acknowledge the possibility that this appears to run contrary to his stated view that we ought to be wary of unnecessarily universalising particular perspectival narratives which express local ethnographic concerns. It is true that prior to the introduction of Philosophical Reasoning and its Categorical concern with Being and Principles (such as noncontradiction and sufficient Reason), the heros narrative was steered by an imaginative idea of the heros journey. But even if our physiology has stayed the same for 40,000 years as Campbell claimed, the organisation of the brain due to the introduction of writing and reading may well be responsible, as Julian Jaynes suggests, for the kind of self-consciousness that has evolved as a human vicissitude of the instincts. We can see clearly in Plato’s writings, the change of emphasis from the virtue of courage to the virtue of wisdom, and the increasing importance of various forms of knowledge insofar as leading the good spirited flourishing life (eudaimonia) was concerned. Achilles excelled in battle, but his courageous life, otherwise did not meet Socratic or Aristotelian criteria. It was Socrates and the mythical Philosophers, returning to the cave from which they originated, that became the new “ideal”, representing wisdom. Whether we can regard these figures as “heros” is not clear. With the advent of philosophers there is an important shift from the individual perspective to the perspective of the polis which, for Socrates, was the soul (psuché) writ large. Socrates was searching for the definition of justice but it was Aristotle who presented us with an essence specifying definition of Man, namely rational animal capable of discourse which transcended the old ideal of the courageous warrior, and perhaps the so called archetype of the hero dissipated with Aristotelian Rationalism and the telos of the contemplative life.
Socrates’ life was, however, in the old sense “heroic” because it ended the way it did for the reasons that it did, but it was not the battlefield but the agora which was the scene of his activities. Challenging those who thought they knew and who were trying to make the worse argument seem the better, of course, took both courage and wisdom. Socrates, like Jesus, knew the risks he was taking in attempting to persuade people to “know thyself!”. What happened to Socrates proved that the Athenian system was not quite equipped to handle appeals to “the child of the Gods”, namely Philosophy. Aristotle too, became persona non grata and was forced to flee from Athens. There is an argument for the position that the polis as a constitutional entity was not equipped to meet the demands for the “new ideals” the Philosophers were arguing for, namely justice, knowledge, and freedom. An interesting footnote to this discussion is the attempt of Alexander the Great, Aristotle’s pupil, to establish a Greek Empire, thereby helping to destabilise the existing system of polis/states. In the spirit of the Aristotelian principle of the Golden Mean, it is worth pointing out that during Kant’s time, neither cities nor empires, but nations became the entities with constitutions.
Campbell in the Preface to his 1949 edition of “The Hero with a thousand faces” refers to a Freudian critique of religion and mythology:
“The Truths contained in religious doctrines are after all so distorted and systematically disguised that the mass of humanity cannot recognise them as truth. The case is similar to what happens when we tell a child that new-born babies are brought by the stork. Here too, we are telling the truth in symbolic clothing, for we know what the large bird signifies. But the child does not know it. He hears only the distorted part of what we say, and feels he has been deceived: and we know how often his distrust of the grown-ups, and his refractoriness actually take their start from this impression. We nave become convinced that it is better to avoid such symbolic disguisings of the truth in what we tell the children and not to withhold from them a knowledge of the true state of affairs commensurate with their intellectual level.” (Pages 44-45)
Freud’s point was, according to Campbell, that the ancient muses knew what they were talking about and which metaphors to use to carry their message further. We moderns, however, need to learn again the “grammar of the symbols”. Campbell adds:
“as a key to this mystery I know of no better modern tool than psychoanalysis.”(The Hero with a thousand faces” (Page xii)
Psychoanalysis, however, has a complex history with roots both in Aristotelian Hylomorphism and Kantian Critical Philosophy, but it is perhaps the latter that is especially relevant to this discussion, given the Freudian declaration that he was a “Kantian Psychologist”. Alongside these relevant facts, however, there is also the deliberate Freudian choice of terminology drawn from Platonic Philosophy, e.g. Eros, Thanatos, Ananke, logos, which clearly transcend the technical language Freud uses to characterise the treatment of his patients. The Freudian theory of the “psychic-apparatus” and its possession of psychological powers in relation to the external world, also manifests elements of Greek thinking that presupposed the Greek view of psuché embedded in a categorical framework of areté, dike, arché, epistemé, aletheia and eudaimonia. In this Philosophical/technical framework there is no clear role for narratives of heros and their quests. The heros quest for self- transformation often contains the occurrence of supernatural events in which tremendous forces are overcome by a superhuman will and determination, communicating perhaps the narcissistic message that “anything is “possible” for such men. The Aristotelian process of self- actualisation is not embedded in a narrative or a story, but is rather part of a philosophical account of the cultural development of a number of powers of human psuché, including the powers of discourse and rationality which are integrated with a number of other psychological/mental powers or functions that in turn have important relations to the external world.
It was Plato that initiated this transition from the form of the narrative to a more enlightened philosophical form of “Philosophical dialogues” featuring the “ very real character” of Socrates, whose mode of being was one of self-efacement rather than self-proclamation. His power of persuasion was considerable, because it was founded upon areté, arché, episteme dike, aletheia, logos, and eudaimonia. One can, if one so desires, read the episodes of the dialogues in terms of the adventures of Socrates, but that would be to miss the pedagogical point of the dialogues, which was to herald in the new era of the new ideals of principles and rationality, emphasising simultaneously the rejection of heros and the rejection of the strategy of making the worse argument seem the better.
The heroic narrative is at best an exercise of the imagination and emotion in the name of the good spirited flourishing life of the individual which, in an aesthetic context, carries the subjective message of exemplary universality and necessity articulated in Kant’s Third Critique. It is true that the trilogy of dialogues, Euthyphro, Apology and Phaedo, seemingly promote a narrative of the Socratic journey to his final destination in a death-cell. The message of these dialogues, however, is more complex. A man who has dedicated his life to justice is convicted for attempting to make citizens aware of the essence of Justice. Socrates at no point proclaimed himself to be a hero or a saviour, and he did not proclaim directly that Philosophy could save us from the Delphic prophecy of ruin and destruction. He nevertheless, over time, became a symbol for the necessity and transcendence of Philosophy.
Athens was the home of three of the greatest Philosophers in history, in relatively rapid succession, and their bond of connection was a sacred one: that of teacher-pupil. Plato incorporated the spirit of Socrates into his dialogues, and Aristotle incorporated the spirits of both Socrates and Plato into his writings. Campbells account of the heros journey has a very different structure, which it can be argued, was promoted into a cult of the hero by Thomas Carlysle, which in turn was transformed into the Hegelian idea of world historical individuals such as Napoleon . This underwent a further transformation into Nietzsches “Will to power”. Associated ideas of “Domination” and Colonisation” were political ideals that have been embraced by a number of modern tyrants since Napoleon. The Greek political heritage, however, probably lies closer to Schopenhauers “will to live” and Kant’s “good will”. Its epistemological heritage encourages a belief in “scientific” explanation/justification. Its artistic heritage includes a belief in the importance of Art and its associated ideals of the beautiful and sublime.
Campbell was undoubtedly a significant explorer of the breadth and depth of psuché via the linking of distant mythologies such as that of the Navaho and Hinduism. His arguments are sometimes hylomorphic and sometimes Kantian but they lack an important philosophical dimension which we have attempted to articulate. It is true as Campbell maintains that mans physiology has not altered for 40000 years but mans most important organ is his brain and the organisation of the functions of that organ may have changed during this period. Language, Julian Jaynes has argued was originally a bilateral function like all the other physiological functions of the brain. The science of physiology teaches us that an organ can lose one function and acquire another. In the case of the origins and history of the function of language, Jaynes has interesting theories to contribute:
“Language, Jaynes argues, began as an expressive phenomenon partly connected to events of importance in the external world /e.g. hunting, and gathering). By a charted series of functions, this developmental sequence eventually reaches the level or representative thought in which we find the names for animals developing into a more complex stage in which names are given to individual people. At this stage it would be fair to say that we are definitely thinking something. As group life evolved we then find language evolving into more complex forms via the use of sentences with subject-predicate structures which illustrate the fully mental power of thinking something about something which Heidegger called the veritative (truth-making) synthesis. This, however is not the final level of the Mental which is achieved only when the principles of Logic and Truth tables begin to constitute and regulate the field of sound argumentation—the field of rationality. These higher mental operations are undoubtedly inhabitants of the realm of the mental being essentially connected to the telos of self-conscious thought.” (James, M.R.,D., The World Explored, the World suffered: A Philosophical istory of Psychology, Cognition, Emotion, Consciousness, and Action: Volume four, Page 194)
This is a hylomorphic account of the development and integration of human psychological powers that are implied by the essence specifying definition of human psuché, namely rational animal capable of discourse. Whilst different languages spoken by different races of man with different histories compel us to attend to these differences, biological reflection focuses upon what we, who are different in certain respects, have in common. In simple primitive environments consciousness may not have possessed the same level of complexity, but mythical narratives certainly appealed to the powers of the imagination and sensibility, quickening in those who had the requisite capacities, an experience of transcendence. Primitive man certainly used myths to orient himself in his environment as well as to begin the attempt to know himself. Campbell claims in this context:
“The symbols of mythology are not manufactured: they cannot be ordered, invented or permanently suppressed. They are spontaneous productions of the psyche, and each bears within it, undamaged, the germ power of its source.” (The Hero with a thousand faces, Page 2)
Many scientific disciplines contribute to our understanding of primitive man and his primitive form of life and Campbell invokes psychoanalysis amongst these. He refers to the long childhood of man, and the subsequent long period of dependence upon our care-givers. As the repertoire of human psychological and mental powers develop much can go awry to disturb this development, and identification of the causes of psychological or mental health problems are not always straightforward matters. One image which the Ancient Greeks use to provide us with an understanding of the human self actualisation process is that of the labyrinth, and psychoanalysis certainly provides us with one of the threads leading out of the cave and into the sunlight. Myth and Religion too provides us with such a thread as does Philosophy.
In an interview entitled “The Road of Trials” Campbell refers to James Joyce and the Arts as responsible for awakening in them the realisation of the universal meaning of the symbols we find in our Myths. In this context he also refers to Hinduism which already in the 9th century BC acknowledged that:
“all the deities are projections of psychological power, and they are within you and not out there. They’re out there also, in a certain way, in a mysterious way but the real place for them is in here (points to the heart).” (Pages 36-37)
James Joyce helped Campbell understand the Eastern texts and laid the foundation for the next phase of his journey, in which he discovered Freud, Jung, and Thomas Mann whilst studying Sanskrit. Yet it was another German Psychologist whom he met in 1981 who would play a large part in helping him to synthesise ideas from Myth, Art, Psychology and Literature, and relate these ideas to the fundamental problem of life, which is:
“to become transparent to transcendence: so that you realise that you are yourself a manifestation of this” (Campbells The Hero’s Journey, Page 51).
Campbell spent one hour with Karlfried Graf Durckheim from Freiburg and emerged from this meeting with a definition of myth as:
“a metaphor transparent to transcendence” (Page 51)
The Ancient Greek spirit of aletheia hovers over all these reflections because it is clear that we are in a world of symbolic language which carries us beyond the normal concerns of speech into the “realm of the sacred”, which is the realm of psuché (life) in which we feel at one with the Universe and especially with all forms of life. Schopenhauer, following Kant, highlighted this aspect of metaphysics when he pointed to the phenomenon of humans sacrificing their lives to save the lives of others, thereby transcending Spinoza’s principle of self preservation in which it is claimed all things strive to preserve themselves in existence.
Views: 243
Ebook:
Audiobook:
https://play.google.com/store/audiobooks/details?id=AQAAAEBy7FSsNM
Podcast
Views: 328


Audiobook: https://play.google.com/store/audiobooks/details?id=AQAAAEDyrGrsiM
EBOOK:
PODCAST Season 6 Episode 4 Conclusion